
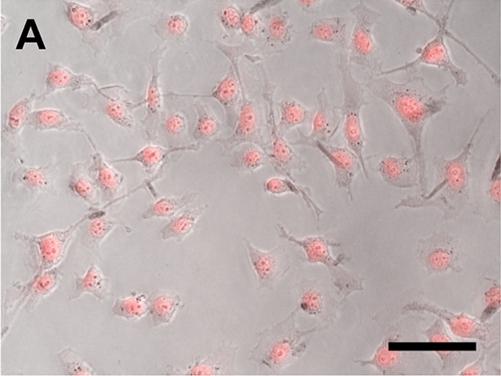
The cells in this image have turned fluorescent pink, showing that the new drug delivery system results in high cellular uptake after being irradiated by near infrared light.
Credit: Jennifer West, Duke University
In a move akin to adding chemical weapons to a firebomb, researchers at Duke University have devised a method for making a promising nanoscale cancer treatment even more deadly to tumors.
The invention allows an extremely thin layer of hydrogels (think contact lenses) to be deposited on the surface of nanoshells — particles about a hundred nanometers wide designed to absorb infrared light and generate heat. When heated, these special hydrogels lose their water content and release any molecules (such as drugs) trapped within.
By depositing the hydrogels on tumor-torching nanoshells and loading the new coating with chemotherapeutic drugs, a formidable one-two punch is formed.
The technique is described in a paper published in the journal ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering on July 13, 2015, and was highlighted as an ACS Editor's Choice.
“The idea is to combine tumor-destroying heat therapy with localized drug delivery, so that you can hopefully have the most effective treatment possible,” said Jennifer West, the Fitzpatrick Family University Professor of Engineering at Duke, who holds appointments in biomedical engineering, mechanical engineering and materials science, cell biology, and chemistry. “And many chemotherapeutic drugs have been shown to be more effective in heated tissue, so there's a potential synergy between the two approaches.”
The photothermal therapy is already in clinical trials for several types of cancers being conducted by Nanospectra Biosciences, Inc., a company West founded. The nanoshells are tuned to absorb near-infrared light, which passes harmlessly through water and tissue. The nanoshells, however, quickly heat up enough to destroy cells, but only where the light shines.
Besides being able to accurately target specific locations in the body with the light, the treatment also hinges on the fact that nanoshells tend to accumulate within a tumor due to leaky vasculature.
“But you have to keep their size under about 500 nanometers,” said West. “We had to come up with a new process to create a very thin polymer coating on the surface of these nanoparticles to keep them under that threshold.”
In the new study, West and doctoral student Laura Strong loaded the newly coated nanoshells with a potent chemotherapeutic drug and delivered them to tumor cells in a laboratory setting. The treatment worked as planned; the nanoshells heated up and destroyed most of the tumor cells while releasing the drugs, which cleaned up the survivors. Completely eradicating every cancerous cell is extremely important, as the escape of even a single cell capable of metastasizing could prove deadly down the road.
The next step for the new cancer treatment is tests in live animals. While those experiments are in progress, human trials are still at least a couple years away.
But the technology need not be limited to cancer therapy.
“The hydrogels can release drugs just above body temperature, so you could potentially look at this for other drug-delivery applications where you don't necessarily want to destroy the tissue,” said West. “You could do a milder warming and still trigger the drug release.”
###
This research was supported by the National Institutes of Health (T32EB009379 and U54CA151668).
“Hydrogel-Coated Near Infrared Absorbing Nanoshells as Light-Responsive Drug Delivery Vehicles.” Laura E. Strong and Jennifer L. West. ACS Biomaterials, 2015. DOI: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.5b00111












