
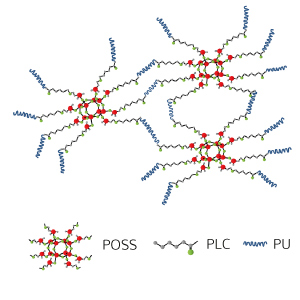
Schematic representation of the star-shaped polymer network showing the polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) cores and crosslinked polycaprolactone (PCL)–polyurethane (PU) arms.
Copyright : Adapted by A*STAR with permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: NPG Asia Materials (Ref. 1), copyright (2014)
Tissues and organs in the body are sometimes damaged to such an extent that they require artificial support to heal. Now, A*STAR researchers have used star-shaped polymers to produce a three-dimensional network that is both compatible with human tissue and facilitates cells to adhere and proliferate under controlled biological conditions[¹].
To build this network, Ming-Yong Han, Khin Yin Win and co-workers from the A*STAR Institute of Materials Research and Engineering in Singapore incorporated an inorganic component ― polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) ― into a common tissue engineering material, polycaprolactone–polyurethane.
This addition was designed to enhance the material’s porosity and interaction with cells as well as improve its thermal and mechanical stability. POSS consisted of a silica cube bearing eight organic arms capable of covalent bonding with other polymers (see image). The silica cube provided a rigid core from which emerged polycaprolactone–polyurethane arms.
To generate this material, the researchers synthesized POSS cores terminated by reactive functional groups from an organic alcohol, in the presence of a silicon-based catalyst. They then attached polycaprolactone units to the cores to extend their arms. Finally, they added the polyurethane precursor as a crosslinker to complete the network.
Unlike its linear counterpart, the POSS-based material had a rough surface consisting of microscopic spheres from which fibrous structures spread. The unique surface morphology, which consisted of water-repelling POSS and polymer arms, helped the cells to adhere and proliferate. This biomaterial was biocompatible and had a high porosity; these properties allowed the material to promote cell growth while simultaneously permitting the exchange of nutrients and metabolites.
The researchers evaluated the degradation of the polymer network under physiological conditions for 52 weeks. The network decomposed little during the first 24 weeks, but subsequently lost weight rapidly.
Han explains that the water-repelling nature and protective effect of the POSS moieties limited the initial hydrolytic degradation. “The degradation accelerated only after these POSS moieties had broken down,” he adds.
This degradation behavior enables cell adhesion and proliferation on the network during the initial stage and elimination of the scaffold after tissue has formed, making the POSS-based network highly attractive as a scaffold. Moreover, most cells remained viable when exposed to the degradation products of these POSS-based and linear polymers, confirming their biocompatibility.
The team is currently exploring ways to apply the star-shaped polymer as a scaffold for tissue regeneration. “We are planning to use it for three-dimensional tissue reconstruction and modeling,” says Han.
The A*STAR-affiliated researchers contributing to this research are from the Institute of Materials Research and Engineering.
Reference
1. Teng, C. P., Mya, K. Y., Win, K. Y., Yeo, C. C., Low, M., He, C. & Han, M.-Y. Star-shaped polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane-polycaprolactone-polyurethane as biomaterials for tissue engineering application. NPG Asia Materials 6, e142 (2014). |
Associated links
http://www.research.a-star.edu.sg/research/7294















