
Oxygen’s Role in Boosting High-Entropy Alloys’ Strength and Ductility
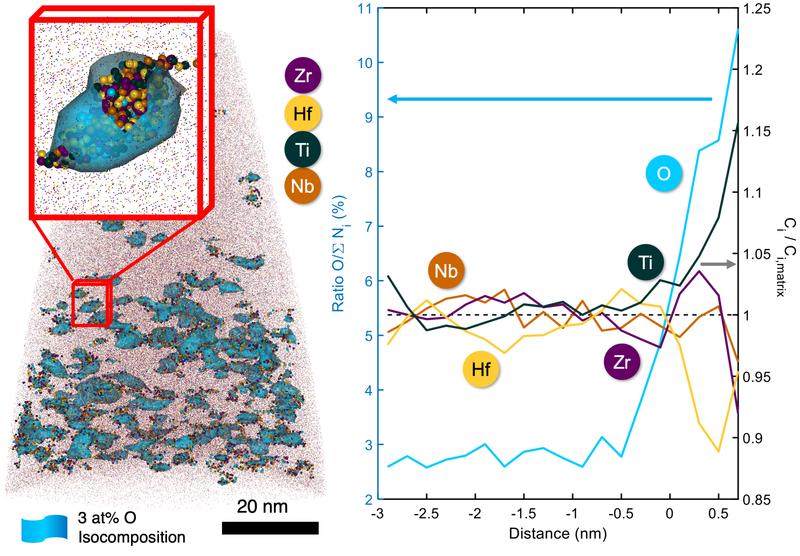
Atom probe tomography reveals a large distribution of ordered oxygen complexes in the model high-entropy alloy investigated.
B. Gault, Max-Planck-Institut für Eisenforschung GmbH
Researchers from the Max-Planck-Institut für Eisenforschung, Düsseldorf, and the University of Science and Technology Beijing discovered a new mechanism that enhances both the antagonistic strength and ductility in a high-entropy alloy.
The new mechanism is caused by the addition of oxygen in relatively high quantity, which alters the alloy’s microstructure and leads to an increase of strength by almost 50% and ductility of ca. 95%. The scientists published their latest findings in Nature.
Oxygen, which is usually neglected as an alloying element as it is known to cause embrittlement, is now added by 2.0 atomic percent in a model high entropy alloy (HEA) of TiZrHfNb.
The researchers studied the effect of oxygen on the microstructure of the HEA to understand the impact on strength and ductility.
They used different analysis techniques such as synchrotron high-energy X-ray diffraction, electron backscatter diffraction mapping and aberration corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) high-angle annular dark field but could not find differences between the oxygen loaded HEA and a usual one.
Only STEM bright field and atom probe tomography revealed the main reason for the spectacular increase in strength: the oxygen is located at interstitial positions within agglomerations of lighter atom , i.e. Ti and Zr.
“We could reveal that the oxygen locates within zones containing only a handful of atoms that are enriched in Ti, and, to a lesser extent Zr. Within these zones, the oxygen is arranged in a highly ordered manner forming individual trapping barriers. At the same time the ductility is increased during deformation when these ordered complexes are cut by dislocations, which are the crystalline defect that carry the plasticity, and cause their multiplication and change the way they shear the crystalline lattice.”, explains Dr. Baptiste Gault, head of the “Atom Probe Tomography” group at the MPIE. The oxygen complexes act as small precipitates and cause a change from planar to wavy slip during deformation.
The presented alloy is a model system, exhibiting too little oxidation resistance. Research to improve their performance by adding Al, Si or Cr is ongoing. The interstitial complex strengthening mechanism could be forming in many other alloy classes beyond HEAs. The scientists are exploring other metallic systems in which the strengthening effects from these ordered complexes could be exploited, in particular alloys that are closer to engineering applications. The work was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of China.
Dr. Baptiste Gault, gault@mpie.de
Z. Lei, X. Liu, Yua. Wu, H. Wang, S. Jiang, S. Wang, X. Hui, Y. Wu, B. Gault, P. Kontis, D. Raabe, L. Gu, Q. Zhang, H. Chen, H. Wang, J. Liu, K. An, Q. Zeng, T. Nieh, Z. Lu
Enhanced strength and ductility in a high-entropy alloy via ordered oxygen complexes
Nature 563 (2018)
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0685-y















