
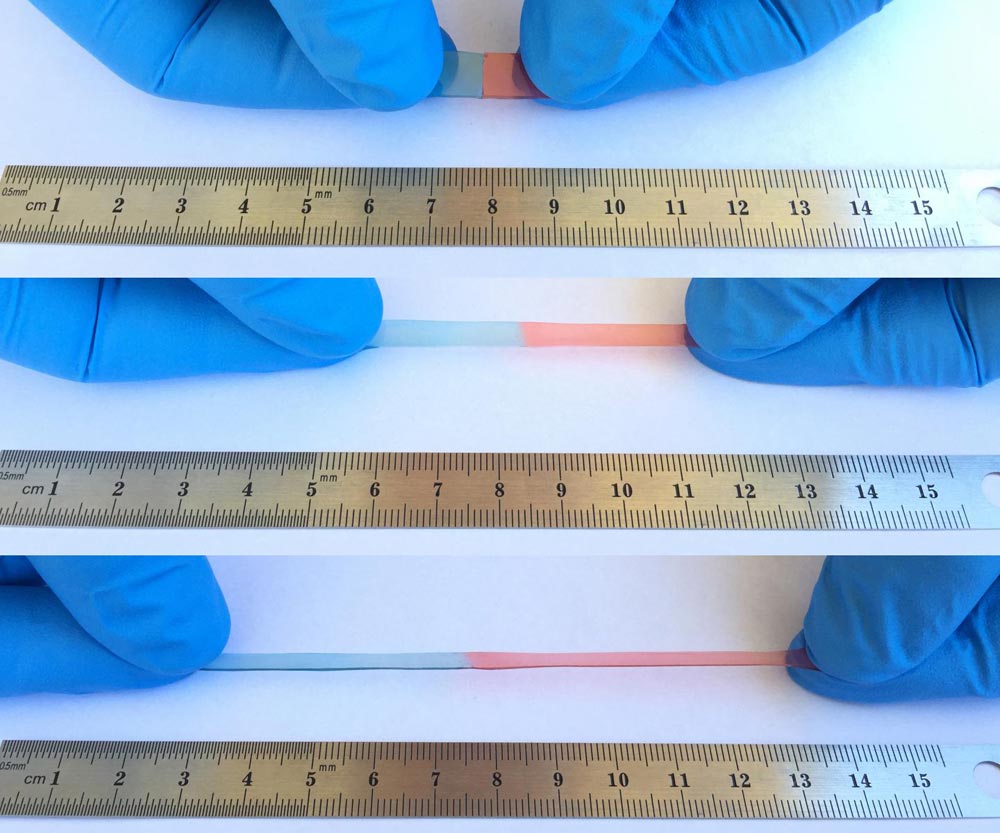
A new material not only heals itself, but it also stretches up to 50 times its usual size; these properties could fix your phone's battery if it cracks or prevent it from breaking in the first place.
Credit: Wang lab
The researchers will present their work today at the 253rd National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS, the world's largest scientific society, is holding the meeting here through Thursday. It features more than 14,000 presentations on a wide range of science topics.
“When I was young, my idol was Wolverine from the X-Men,” Chao Wang, Ph.D., says. “He could save the world, but only because he could heal himself. A self-healing material, when carved into two parts, can go back together like nothing has happened, just like our human skin. I've been researching making a self-healing lithium ion battery, so when you drop your cell phone, it could fix itself and last much longer.”
The key to self-repair is in the chemical bonding. Two types of bonds exist in materials, Wang explains. There are covalent bonds, which are strong and don't readily reform once broken; and noncovalent bonds, which are weaker and more dynamic. For example, the hydrogen bonds that connect water molecules to one another are non-covalent, breaking and reforming constantly to give rise to the fluid properties of water. “Most self-healing polymers form hydrogen bonds or metal-ligand coordination, but these aren't suitable for ionic conductors,” Wang says.
Wang's team at the University of California, Riverside, turned instead to a different type of non-covalent bond called an ion-dipole interaction, a force between charged ions and polar molecules. “Ion-dipole interactions have never been used for designing a self-healing polymer, but it turns out that they're particularly suitable for ionic conductors,” Wang says. The key design idea in the development of the material was to use a polar, stretchable polymer, poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene), plus a mobile, ionic salt. The polymer chains are linked to each other by ion-dipole interactions between the polar groups in the polymer and the ionic salt.
The resulting material could stretch up to 50 times its usual size. After being torn in two, the material automatically stitched itself back together completely within one day.
As a test, the researchers generated an “artificial muscle” by placing a non-conductive membrane between two layers of the ionic conductor. The new material responded to electrical signals, bringing motion to these artificial muscles, so named because biological muscles similarly move in response to electrical signals (though Wang's materials are not intended for medical applications).
For the next step, the researchers are working on altering the polymer to improve the material's properties. For example, they are testing the material in harsh conditions, such as high humidity. “Previous self-healing polymers haven't worked well in high humidity, Wang says. “Water gets in there and messes things up. It can change the mechanical properties. We are currently tweaking the covalent bonds within the polymer itself to get these materials ready for real-world applications.”
###
A press conference on this topic will be held Tuesday, April 4, at 10 a.m. Pacific time in the Moscone Center. Reporters may check-in at the press center, South Building, Foyer, or watch live on YouTube http://bit.
Wang acknowledges funding from start-up funds from the University of California, Riverside.
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With nearly 157,000 members, ACS is the world's largest scientific society and a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. ACS does not conduct research, but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive press releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note to journalists: Please report that this research was presented at a meeting of the American Chemical Society.
Title
Mechanically adaptive electronic polymers for transparent self-healing artificial muscle
Abstract
Electronic polymers are functional materials of central importance to a range of applications spanning from energy storage to electronic devices. Additional applications are emerging in new areas of research including stretchable electronics and soft robotics, where electronic conductors are required to be stretchable. Take the polymer ionic conductors for one example. While a substantial amount of research has addressed the electronic properties of ionic conductors, there is a clear lack of research addressing the mechanical properties of ionic conductors. In particular, applications that require high stretchability and that experience significant mechanical wear would strongly benefit from the integration of self-healing capabilities in order to extend lifetime and lower cost of devices.
This paper introduces a transparent, self-healing, ionically conductive elastomer, that tolerates extreme strains (>5000%), has an ionic conductivity of 10-4 S cm-1 and is highly transparent across the visible spectrum (average transmittance of 92%). The material can fully heal from severe mechanical damage within 24 hours at room temperature. We demonstrate the unique properties of the ionically conductive elastomer by using it to fabricate self-healing transparent artificial muscles.















