
MIPT researchers grow cardiac tissue on 'spider silk' substrate
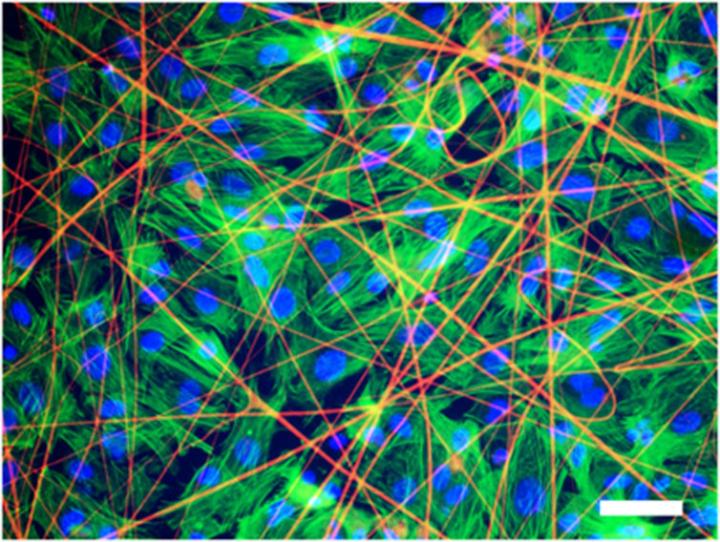
These are heart tissue cells grown on a matrix, stained with fluorescent markers.
Credit: © Alexander Teplenin et al. / PLOS ONE
The cultivation of organs and tissues from a patient's cells is the bleeding edge of medical research – regenerative methods can solve the problem of transplant rejection. However,it's quite a challenge to find a suitable frame, or substrate, to grow cells on.
The material should be non-toxic and elastic andshould not be rejected by the body or impede cell growth. A group of researchers led by Professor Konstantin Agladze, who heads the Laboratory of the Biophysics of Excitable Systems at MIPT, works on cardiac tissue engineering. The group has been cultivating fully functional cardiac tissues, able to contract and conduct excitation waves, from cells called cardiomyocytes.
Previously, the group used synthetic polymeric nanofibers but recently decided to assay another material – electrospunfibers of spidroin, the cobweb protein. Cobweb strands are incredibly lightand durable. They're five times stronger than steel, twice more elastic than nylon, and are capable of stretching a third of their length. The structure of spidroin molecules that make up cobweb drag lines is similar to that of the silk protein, fibroin, but is much more durable.
Researchers would normally use artificial spidroin fiber matrices as a substrate to grow implants like bones, tendons and cartilages, as well as dressings. Professor Agladze's team decided to find out whether a spidroin substrate derived from genetically modified yeast cells can serve to grow cardiac cells.
For this purpose, they seeded isolated neonatal rat cardiomyocytes on fiber matrices. During the experiment, the researchers monitored the growth of the cells and tested their contractibility and the ability to conduct electric impulses, which are the main features of normal cardiac tissue.
The monitoring, carried out with the help of a microscope and fluorescent markers, showed that within three to five days a layer of cells formed on the substrate that were able to contract synchronously and conduct electrical impulses just like the tissue of a living heart would.
“We can answer positively all questions we put at the beginning of this research project,” Professor Agladze says. “Cardiac tissue cells successfully adhere to the substrate of recombinant spidroin; they grow forming layers and are fully functional, which means they can contract coordinately.”












