
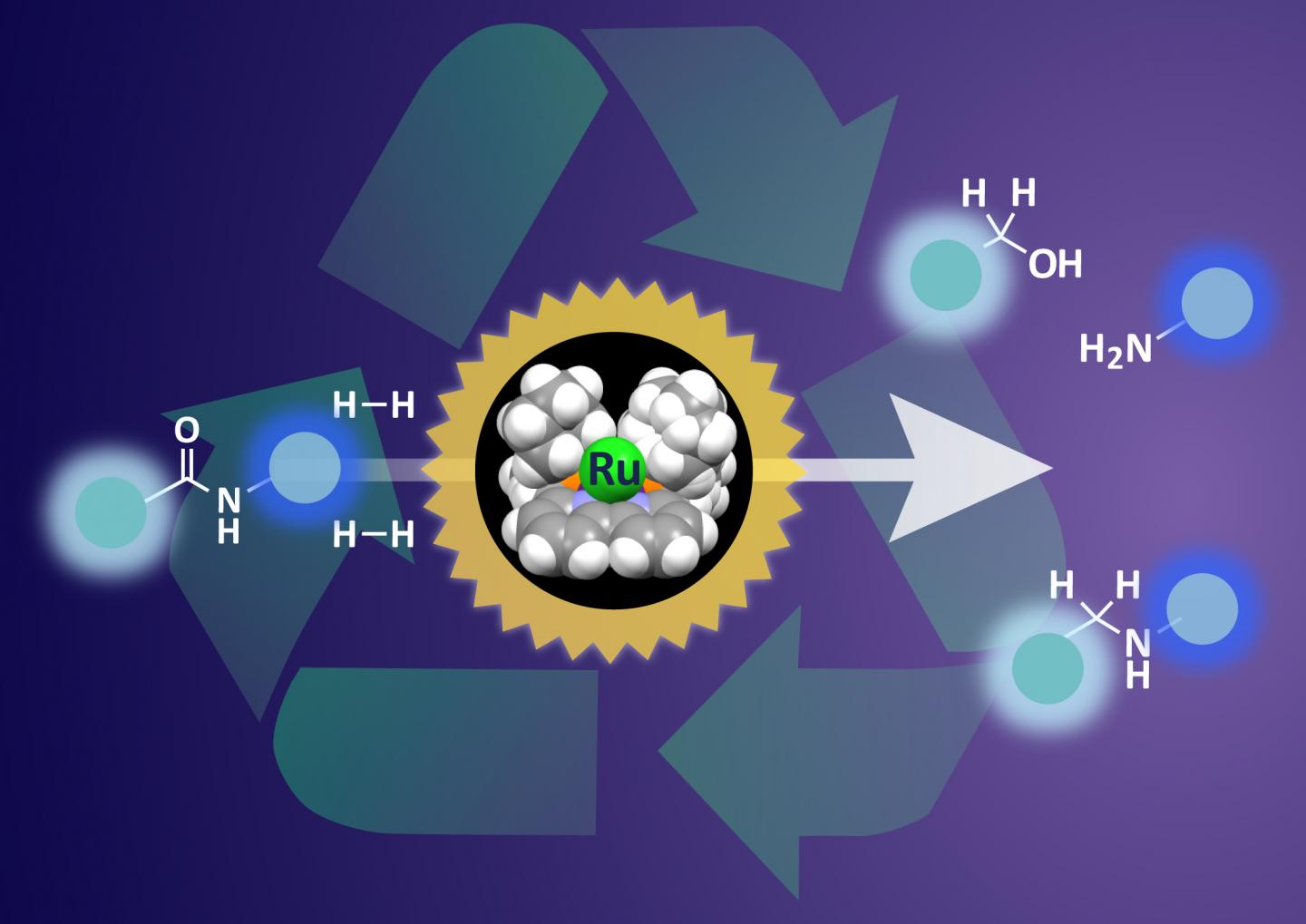
Design of a sterically confined bipyridine-ruthenium (Ru) framework allows controlled confinement of adsorbed H2 and its delivery to inert amides enabling catalytic hydrogenation of a wide range of amide bonds. Cleavage of both C=O and C-N lactam bonds achieved by activation of a single precatalyst.
Credit: Nagoya Univesity
Nagoya, Japan – What to do proteins and Kevlar have in common? Both feature long chain molecules that are strung together by amide bonds. These strong chemical bonds are also common to many other naturally occurring molecules as well as man-made pharmaceuticals and plastics.
Although amide bonds can give great strength to plastics, when it comes to their recycling at a later point, the difficultly of breaking these bonds usually prevents recovery of useful products. Catalysts are widely used in chemistry to help speed up reactions, but breaking the kinds of amide bonds in plastics, such as nylon, and other materials requires harsh conditions and large amounts of energy.
Building on their previous work, a research team at Nagoya University recently developed a series of organometallic ruthenium catalysts to break down even the toughest amide bonds effectively under mild conditions.
“Our previous catalysts could hydrogenate most amide bonds, but the reactions needed a long time at high temperature and high pressure. This new ruthenium catalyst can hydrogenate difficult substrates under much milder conditions,” says lead author Takashi Miura.
Hydrogenation is the key step leading to breakdown of amide bonds. The catalyst features a ruthenium atom supported in an organic framework. This ruthenium atom can adsorb hydrogen and deliver it to the amide bond to initiate the breakdown.
The team probed the position of hydrogen on the catalyst in the reaction pathway and modified the shape of the supporting framework. By making sure that the hydrogen molecule was is the best possible position for interaction with amide bonds, the team achieved much more effective hydrogenation.
Group leader Susumu Saito says, “The changes we made to the catalyst allowed some tricky amide bonds to be selectively cleaved for the first time. This catalyst has great potential for making designer peptides for pharmaceutics and could also be used to recover materials from waste plastics to help realize an anthropogenic chemical carbon cycle.”
###
The article, “Multifaceted catalytic hydrogenation of amides via diverse activation of a sterically confined bipyridine-ruthenium framework” was published in Scientific Reports at DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-01645-z












