
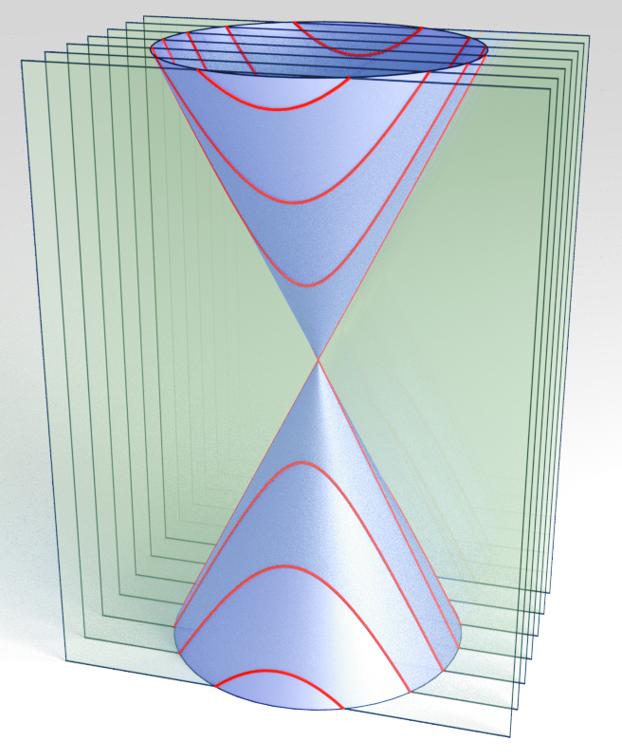
This is a dirac cone showing a typical dispersion relation (energy vs. momentum) for 2-D graphene material. Red cross-sectional lines represent quantization of the energy (and momentum) due to a finite size constriction.
Credit: B. Terrés, L. A. Chizhova, F. Libisch, J. Peiro, D. Jörger, S. Engels, A. Girschik, K. Watanabe, T. Taniguchi, S. V. Rotkin, J. Burgdörfer, C. Stampfer
Quantum mechanics is the field of physics governing the behavior of things on atomic scales, where things work very differently from our everyday world.
One of the most direct manifestations of quantum mechanics is quantization. Quantization results in the discrete character of physical properties at small scales, which could be the radius of an atomic orbit or the resistance of a molecular wire. The most famous one, which won Albert Einstein the Nobel Prize, is the quantization of the photon energy in the photoelectric effect– the observation that many metals emit electrons when light shines upon them.
Quantization occurs when a quantum particle is confined to a small space. Its wave function develops a standing wave pattern, like waves in a small puddle. Physicists then speak of size quantization: the energy of the particle may only take those values where the nodal pattern of the standing wave matches the system boundary.
A striking consequence of size quantization is quantized conductance: the number of particles that can simultaneously traverse a narrow corridor, a so-called nanoconstriction, become discrete. As a result the current through such a constriction is an integer multiple of the quantum of conductance.
In a recent joint experimental and theoretical work, an international group of physicists demonstrated size quantization of charge carriers, i.e. quantized conductance in nanoscale samples of graphene. The results have been published in an article called “Size quantization of Dirac fermions in graphene constrictions” in Nature Communications.
The high-quality material graphene, a single-atomic layer of carbon, embedded in hexagonal boron nitride demonstrates unusual physics due to the hexagonal–or honey comb–symmetry of its lattice. However, observing size quantization of charge carriers in graphene nanoconstrictions has, until now, proved elusive due to the high sensitivity of the electron wave to disorder.
The researchers demonstrated quantization effects at very low temperatures (liquid Helium), where the influence of thermal disorder ceases. This new approach–of encapsulating graphene constrictions between layers of boron nitride–allowed for exceptionally clean samples, and thus highly accurate measurements.
At zero magnetic field, the measured current shows clear signatures of size quantization, closely following theoretical predictions. For increasing magnetic field, these structures gradually evolve into the Landau levels of the quantum Hall effect.
“The high sensitivity of this transition to scattering at the constriction edges reveals indispensable details about the role of edge scattering in future graphene nanoelectronic devices,” said Slava V. Rotkin, professor of physics and materials science & engineering at Lehigh University and a co-author of the study.












