The structural memory of water persists on a picosecond timescale
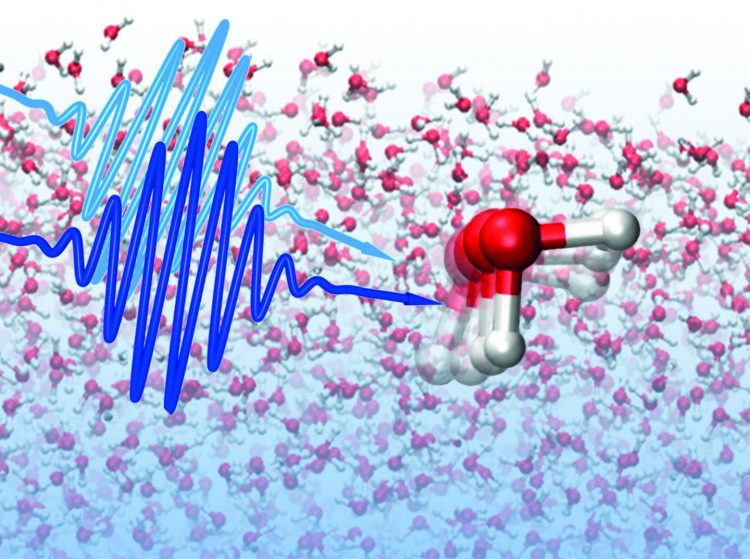
The lifetime of local water structures is probed using ultrafast laser pulses. Credit: © Yuki Nagata / MPI-P
A team of scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research (MPI-P) in Mainz, Germany and FOM Institute AMOLF in the Netherlands have characterized the local structural dynamics of liquid water, i.e. how quickly water molecules change their binding state.
Using innovative ultrafast vibrational spectroscopies, the researchers show why liquid water is so unique compared to other molecular liquids. This study has recently been published in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
With the help of a novel combination of ultrafast laser experiments, the scientists found that local structures persist in water for longer than a picosecond, a picosecond (ps) being one thousandth of one billionth of a second (10-12 s). This observation changes the general perception of water as a solvent. “71% of the earth's surface is covered with water.
As most chemical and biological reactions on earth occur in water or at the air water interface in oceans or in clouds, the details of how water behaves at the molecular level are crucial. Our results show that water cannot be treated as a continuum, but that specific local structures exist and are likely very important” says Mischa Bonn, director at the MPI-P.
Water is a very special liquid with extremely fast dynamics. Water molecules wiggle and jiggle on sub-picosecond timescales, which make them undistinguishable on this timescale.
While the existence of very short-lived local structures – e.g. two water molecules that are very close to one another, or are very far apart from each other – is known to occur, it was commonly believed that they lose the memory of their local structure within less than 0.1 picoseconds.
The proof for relatively long-lived local structures in liquid water was obtained by measuring the vibrations of the Oxygen-Hydrogen (O-H) bonds in water. For this purpose the team of scientists used ultrafast infrared spectroscopy, particularly focusing on water molecules that are weakly (or strongly) hydrogen-bonded to their neighboring water molecules.
The scientists found that the vibrations live much longer (up to about 1 ps) for water molecules with a large separation, than for those that are very close (down to 0.2 ps). In other words, the weakly bound water molecules remain weakly bound for a remarkably long time.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



