
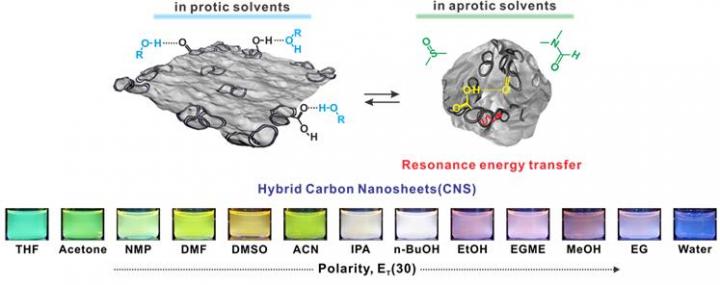
Synthesis and optical properties of hybrid carbon nanosheets (CNSs).
Credit: UNIST
In the study, the joint research team, led by Professor Byung Soo kim and Professor Oh Hoon Kwon has presented a unique design and synthesis of hybrid carbon nanosheets (CNSs), which show a strong solvatochromic behavior with wide color tunability ranging from blue to orange and even to white in various solvents.
This unique hybrid CNS hosts clusters of carbon nanorings on the surface of graphene-oxide (GO) nanosheets as the product of the hydrothermal reaction of small molecular precursors in the presence of GO nanosheets. Moreover, under UV and visible-light excitation, the hybrid CNS exhibits tunable emission spanning the wide range of colors in a series of solvents with different polarities.
According to the research team, this interesting spectroscopic behavior is found to originate from hydrogen-bonding interactions between CNS and solvents, which eventually induce the morphological transition of CNS from 2D sheets to 3D crumpled morphologies, affecting the lifetimes of emissive states.
“The clusters of carbon nanorings on the surface of GO nanosheets have different chemical reactions depending on the properties of solvents,” says Yuri Choi (Combined M.S./Ph.D. student of Natural Science), the first author of the study. “The spectroscopic behavior of CNS is found to originate from hydrogen (H)-bonding interactions between CNS and solvents.”
“This is one of the first studies to show clearly that the shape of CNS varies depending on the solvents,” says Professor Kim. “Through this research, we hope to improve the physical characteristics of hybrid materials and expand its application fields.”
In the study, Professor Kwon and his team analyzed the basic principles of fluorescent light control for CNSs, using time-resolved electronic spectroscopy. In the protic solvent, the structure of CNS showed orange emission was shown due to the loss of energy, caused by the lack of H-bonding within a CNS. On the other hand, it showed the green emission due to less energy lost in the aprotic solvent.
This study has been supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant and by the Institute of Basic Science, Korea. The research team expects that this novel soft carbon nanostructure may open up a new possibility in tailoring the photophysical properties of carbon nanomaterials.
###
Journal Reference
Yuri Choi et al., “Morphology Tunable Hybrid Carbon Nanosheets with Solvatochromism”, Advanced Materials, (2017).












