
Enhancing Cultured Meat: Myoglobin Boosts Color and Texture
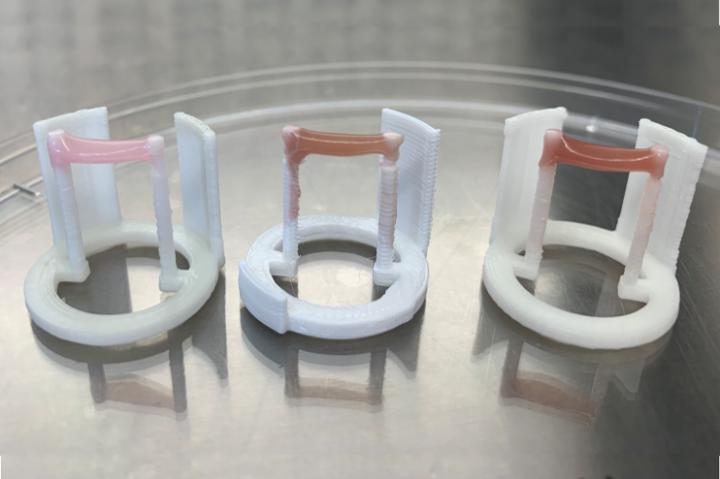
Bovine skeletal muscle cells grown in the presence of myoglobin (center) or hemoglobin (right)
Credit: Robin Simsa & David Kaplan, Tufts University
A team of Tufts University-led researchers exploring the development of cultured meat found that the addition of the iron-carrying protein myoglobin improves the growth, texture and color of bovine muscle grown from cells in culture. This development is a step toward the ultimate goal of growing meat from livestock animal cells for human consumption.
The researchers found that myoglobin increased the proliferation and metabolic activity of bovine muscle satellite cells. Addition of either myoglobin or hemoglobin also led to a change of color more comparable to beef. The results, published today in FOODS, indicate potential benefits of adding heme proteins to cell media to improve the color and texture of cell-grown meat.
“Taste, color, and texture will be critical to consumer acceptance of cultured meat,” said David Kaplan, Stern Family Professor of Engineering at the Tufts University School of Engineering and corresponding author of the study.
“If our goal is to make something similar to a steak, we need to find the right conditions for cells to grow that replicate the formation of natural muscle. The addition of myoglobin looks to be one more important addition to the recipe that brings us closer to that goal,” added Kaplan, chair of the Department of Biomedical Engineering and a program faculty member at the Sackler School of Graduate Biomedical Sciences at Tufts.
The rationale for developing cultured meat (also referred to as 'lab-grown meat', 'cellular agriculture' or 'cell-based meat') is the potential to reduce the amount of resources required in meat production, as well as significantly shrink its environmental footprint relative to animal farming.
Animal farming has been associated with greenhouse gas emissions, antibiotic resistance problems, animal welfare concerns, and land use issues, such as the clearing of the Amazon rainforests.
The ability to grow cultured meat in a bioreactor, as in tissue engineering, could potentially alleviate these issues. However, much remains to be done to grow the cells in a way that replicates the texture, color and flavor of naturally derived meat.
Plant-based meat substitutes like the Impossible Burger have incorporated heme proteins from soy, which make the product more meat-like in appearance and taste. The Tufts-led research team hypothesized that adding heme proteins to meat cell culture could not only have a similar effect but also could improve the growth of muscle cells which require the heme proteins to thrive.
Myoglobin is a natural component of muscle, and hemoglobin is found in blood. As heme proteins, both carry iron atoms that are responsible for the natural bloody, slightly 'metallic' taste of beef. The researchers found that adding hemoglobin or myoglobin changes the color of the bioartificial muscle to a reddish-brown meat-like hue. Myoglobin, however, was much better for promoting cell proliferation and differentiation of the BSCs to mature muscle cells, and better at helping the cells form fibers and adding a rich meat-like color.
“We knew that myoglobin has an important role to play in muscle growth, as it is one of the most abundant proteins in muscle cells” said first author of the study Robin Simsa, an industrial Ph.D. student from Europe who conducted the studies during his fellowship stay at the Tufts University School of Engineering.
“It's possible that myoglobin is bringing oxygen to the cell's mitochondria, boosting their energy and helping them to proliferate. More than just an ingredient for color, iron content and potentially flavor, myoglobin could also be an important element in the scaled-up production of cell-based meat to increase cell yield.”
###
Other authors contributing to the study include John Yuen, Andrew Stout and Natalie Rubio, all graduate students at the Tufts University School of Engineering and working on cellular agriculture goals; and Per Fogelstrand of the University of Gothenburg, Sweden, the PI supervisor for Robin Simsa.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (#P41EB002520) and New Harvest. Simsa was supported by the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Sk?odowska-Curie grant #722779, conducted within the “Training 4 Cell Regenerative Medicine” (T4CRM) network. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Simsa, R., Yuen, J., Stout, A., Rubio, N., Fogelstrand, P., and Kaplan DL. “The role of extracellular hemoglobin and myoglobin in cell-based meat development” FOODS 2019, 8(10), 521, DOI: 10.3390/foods8100521
About Tufts University
Tufts University, located on campuses in Boston, Medford/Somerville and Grafton, Massachusetts, and in Talloires, France, is recognized among the premier research universities in the United States. Tufts enjoys a global reputation for academic excellence and for the preparation of students as leaders in a wide range of professions. A growing number of innovative teaching and research initiatives span all Tufts campuses, and collaboration among the faculty and students in the undergraduate, graduate and professional programs across the university's schools is widely encouraged.












