
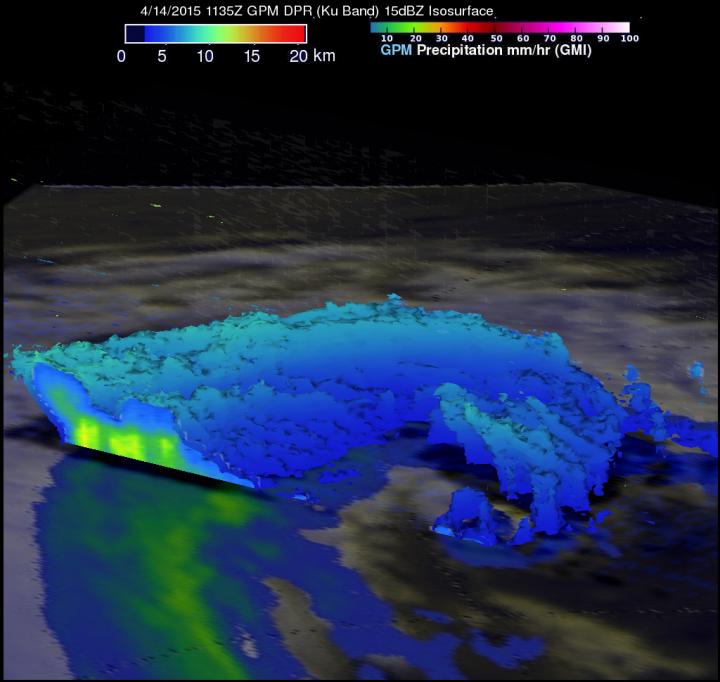
GPM data from April 14 showed that Joalane's highest storm tops were as high as 9.37 km (5.8 miles) in rain bands south of Joalane's center of circulation.
Image Credit: SSAI/NASA, Hal Pierce
The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) core observatory satellite had a last look at the remnants of Tropical Cyclone Joalane on April 14, 2015 at 1135 UTC (4:35 p.m. local time/7:35 a.m. EDT/U.S.).
GPM's Microwave Imager (GMI) instrument found very little rainfall around Joalane's center and light to moderate rainfall in bands on the outer edges of the rapidly weakening tropical cyclone.
At NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, reflectivity data derived from the Ku band on GPM's dual frequency radar was used to create a three-dimensional image of the extra-tropical cyclone.
The 3-D image showed cloud tops were tilted toward the south, clearly indicating how strongly vertical shear was affecting the rapidly weakening tropical cyclone. GPM data showed that Joalane's highest storm tops were as high as 9.37 km (5.8 miles) in rain bands south of Joalane's center of circulation.
Joalane continued to weaken and is expected to dissipate in a day or two.















