
Growing mountains or shifting ground: What is going on in Earth's inner core?
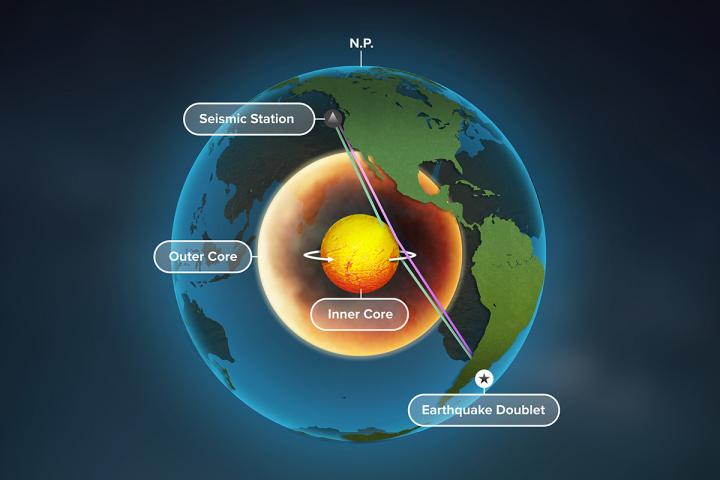
A new study of Earth's inner core used seismic data from repeating earthquakes, called doublets, to find that refracted waves, blue, rather than reflected waves, purple, change over time -- providing the best evidence yet that Earth's inner core is rotating.
Credit: Graphic by Michael Vincent
Usage Restrictions: This graphic may be used in stories related to this press release. Credit is required.
The new study by researchers from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign is published in the journal Earth and Planetary Science Letters.
Geologists do not fully understand how the Earth's magnetic field generator works, but suspect it is closely linked to dynamic processes near the inner core-outer core boundary area, the researchers said. Shifts in the location of the magnetic poles, changes in field strength and anomalous seismic data have prompted researchers to take a closer look.
“In 1996, a small but systematic change of seismic waves passing through the inner core was first detected by our group, which we interpreted as evidence for differential rotation of the inner core relative to the Earth's surface,” said geology professor and study co-author Xiaodong Song, who is now at Peking University.
“However, some studies believe that what we interpret as movement is instead the result of seismic waves reflecting off an alternately enlarging and shrinking inner core boundary, like growing mountains and cutting canyons.”
The researchers present seismic data from a range of geographic locations and repeating earthquakes, called doublets, that occur in the same spot over time.
“Having data from the same location but different times allows us to differentiate between seismic signals that change due to localized variation in relief from those that change due to movement and rotation,” said Yi Yang, a graduate student and lead author of the study.
The team found that some of the earthquake-generated seismic waves penetrate through the iron body below the inner core boundary and change over time, which would not happen if the inner core were stationary, the researchers said.
“Importantly, we are seeing that these refracted waves change before the reflected waves bounce off the inner core boundary, implying that the changes are coming from inside the inner core,” Song said.
The basis of the debate lies in the fact the prior studies looked at a relatively small pool of somewhat ambiguous data generated from a method that is highly dependent on accurate clock time, the researchers said.
“What makes our analysis different is our precise method for determining exactly when the changes in seismic signals occur and arrive at the various seismic stations across the globe,” Yang said. “We use a seismic wave that did not reach inner core as a reference wave in our calculations, which eliminates a lot of the ambiguity.”
This precise arrival time analysis, an extensive collection of the best quality data and careful statistical analysis performed by Yang, are what give this study its power, Song said. “This work confirms that the temporal changes come mostly, if not all, from the body of the inner core, and the idea that inner core surface changes are the sole source of the signal changes can now be ruled out,” he said.
###
The National Science Foundation and the Natural Science Foundation of China supported this study.
Editor's notes:
To reach Xiaodong Song, call 217-714-5125; email xsong@illinois.edu.
The paper “Origin of temporal changes of inner-core seismic waves” is available online and from the U. of I. News Bureau. DOI: 10.1016/j.epsl.2020.116267















