
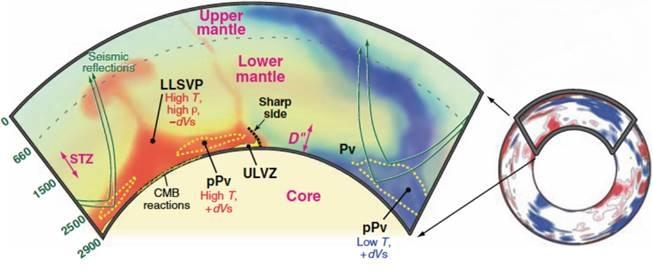
The movement of seismic waves through the material of the mantle allows scientists to image Earth's interior, just as a medical ultrasound allows technicians to look inside a blood vessel. Image is courtesy of Edward Garnero and Allen McNamara's 2008 Science paper Structure and Dynamics of Earth's Lower Mantle, provided with Garnero's permission.
Credit: Edward Garnero and Allen McNamara
New research on oxygen and iron chemistry under the extreme conditions found deep inside the Earth could explain a longstanding seismic mystery called ultralow velocity zones. Published in Nature, the findings could have far-reaching implications on our understanding of Earth's geologic history, including life-altering events such as the Great Oxygenation Event, which occurred 2.4 billion years ago.
Sitting at the boundary between the lower mantle and the core, 1,800 miles beneath Earth's surface, ultralow velocity zones (UVZ) are known to scientists because of their unusual seismic signatures.
Although this region is far too deep for researchers to ever observe directly, instruments that can measure the propagation of seismic waves caused by earthquakes allow them to visualize changes in Earth's interior structure; similar to how ultrasound measurements let medical professionals look inside of our bodies.
These seismic measurements enabled scientists to visualize these ultralow velocity zones in some regions along the core-mantle boundary, by observing the slowing down of seismic waves passing through them. But knowing UVZs exist didn't explain what caused them.
However, recent findings about iron and oxygen chemistry under deep-Earth conditions provide an answer to this longstanding mystery.
It turns out that water contained in some minerals that get pulled down into the Earth due to plate tectonic activity could, under extreme pressures and temperatures, split up–liberating hydrogen and enabling the residual oxygen to combine with iron metal from the core to create a novel high-pressure mineral, iron peroxide.
Led by Carnegie's Ho-kwang “Dave” Mao, the research team believes that as much as 300 million tons of water could be carried down into Earth's interior every year and generate deep, massive reservoirs of iron dioxide, which could be the source of the ultralow velocity zones that slow down seismic waves at the core-mantle boundary.
To test this idea, the team used sophisticated tools at Argonne National Laboratory to examine the propagation of seismic waves through samples of iron peroxide that were created under deep-Earth-mimicking pressure and temperature conditions employing a laser-heated diamond anvil cell. They found that a mixture of normal mantle rock with 40 to 50 percent iron peroxide had the same seismic signature as the enigmatic ultralow velocity zones.
For the research team, one of the most-exciting aspects of this finding is the potential of a reservoir of oxygen deep in the planet's interior, which if periodically released to the Earth's surface could significantly alter the Earth's early atmosphere, potentially explaining the dramatic increase in atmospheric oxygen that occurred about 2.4 billion years ago according to the geologic record.
“Finding the existence of a giant internal oxygen reservoir has many far-reaching implications,” Mao explained. “Now we should reconsider the consequences of sporadic oxygen outbursts and their correlations to other major events in the Earth's history, such as the banded-iron formation, snowball Earth, mass extinctions, flood basalts, and supercontinent rifts.”
###
Other team members including Jin Liu, Qingyang Hu, and Wendy L. Mao of Stanford University; Duckyoung Kim of the Center of High Pressure Science and Technology Advanced Research in China, Zhongqing Wu and Wenzhong Wang of University of Science and Technology of China; Yuming Xiao, Paul Chow, and Yue Meng of Carnegie's High Pressure Collaborative Access Team; and Vitali B. Prakapenka of Center for Advanced Radiation Sources.
This work is supported by the U.S. National Science Foundation, the U.S. Department of Energy, the Deep Carbon Observatory, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
The Carnegie Institution for Science is a private, nonprofit organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with six research departments throughout the U.S. Since its founding in 1902, the Carnegie Institution has been a pioneering force in basic scientific research. Carnegie scientists are leaders in plant biology, developmental biology, astronomy, materials science, global ecology, and Earth and planetary science.















