
NASA-JAXA's TRMM satellite sees rapid intensification of category-5 Marcia
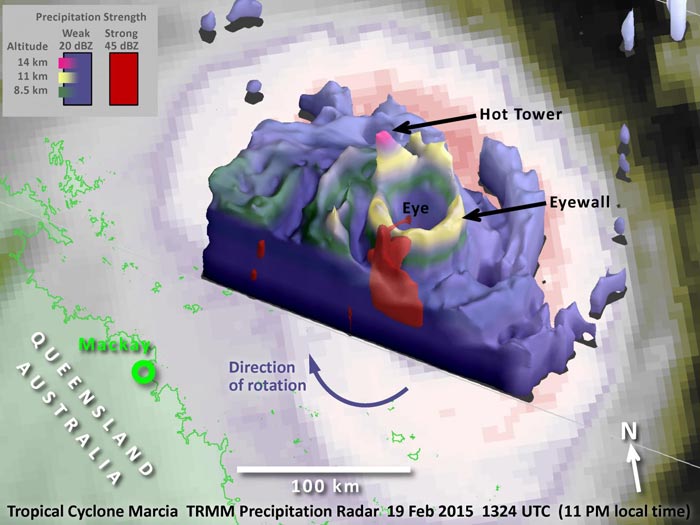
TRMM data showed a hot tower up to 8.6 miles (14 km) high in the northwest quadrant of the eyewall (the purple pinnacle of the outer, blue volume).
Image Credit: NASA/JAXA, Owen Kelley
The TRMM satellite is managed by both NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. The TRMM Precipitation Radar gives three-dimensional information about the tropical storm's eyewall.
In this case, the heavy precipitation (the red volume of the image) near the ocean surface is the powerful base of a hot tower in the southwest quadrant of the eyewall.
A “hot tower” is a rain cloud that reaches at least to the top of the troposphere, the lowest layer of the atmosphere. It extends approximately nine miles (14.5 km) high in the tropics. These towers are called “hot” because they rise to such altitude due to the large amount of latent heat.
Water vapor releases this latent heat as it condenses into liquid. NASA research found that a tropical cyclone with a hot tower in its eyewall was twice as likely to intensify within the next six hours, than a cyclone that lacked a tower.
Since this tropical cyclone is in the southern hemisphere, the winds rotate clockwise (the opposite direction from North Atlantic hurricanes). The updraft in this tower is strong enough to lift precipitation, as it rotates clockwise, up to an 8.6 mile (14 km) altitude in the northwest quadrant of the eyewall (the purple pinnacle of the outer, blue volume).
With infrared satellite imagery, only the tall overshooting top can be seen, leaving one in the dark about what precipitation processes are on-going “under the lid” of the tropical cyclone. Forecasters are particularly interested in these processes when a tropical cyclone is rapidly intensifying near landfall, as is the case with Marcia at the time of this TRMM overflight.
While the TRMM satellite is near the end of its operational lifetime, a more advanced satellite was launched about a year ago that will be able to make 3-D observations of tropical cyclones with a dual-frequency radar and also carries a passive-microwave radiometer. This new satellite is called the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) core satellite.
For more information about TRMM and GPM, visit: http://pmm.















