
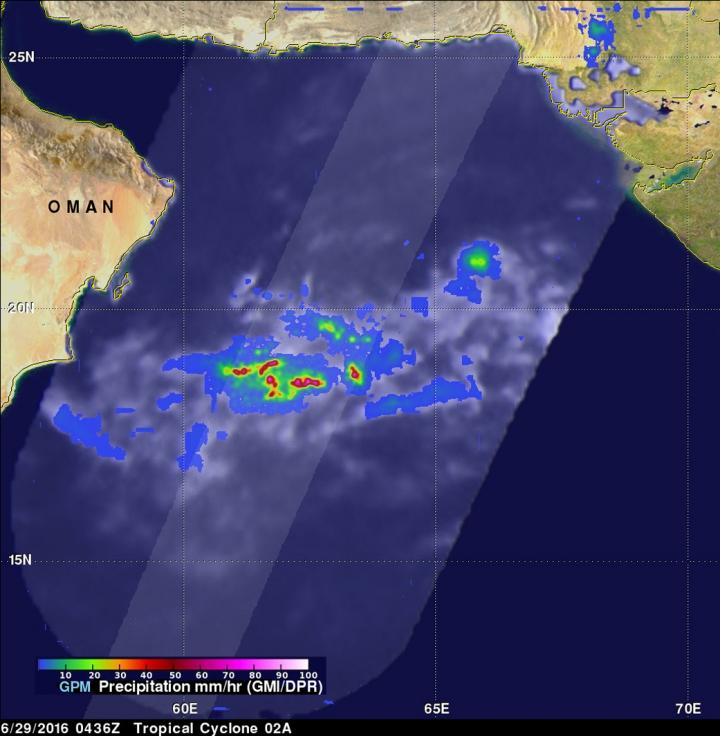
On June 29, GPM showed Tropical Cyclone 02A had a few powerful convective thunderstorms southwest of the center of circulation were dropping rain at the extreme rate of over 209 mm (8.2 inches) per hour.
Credits: NASA/JAXA/SSAI, Hal Pierce
On June 28 at 1800 UTC (2 p.m. EDT) the Joint Typhoon Warning Center issued its final bulletin on Tropical Cyclone 02A.
At that time, the storm had weakened to a depression with maximum sustained winds near 30 knots. It was located about 248 nautical miles east of Masirah Island, Oman. The depression was moving to the south-southwest at 2 knots and weakening.
The GPM core observatory satellite provided an excellent look at rainfall near the tropical cyclone when it passed above on June 29, 2016 at 0436 UTC (12:36 a.m. EDT).
Data collected by GPM's Microwave Imager (GMI) and Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) instruments showed that a few powerful convective thunderstorms southwest of the weakening tropical cyclone's center of circulation were dropping rain at the extreme rate of over 209 mm (8.2 inches) per hour.
The lighter shaded swath on the GPM satellite view indicates the area covered by GPM's radar.
The GPM satellite's Radar (DPR Ku Band) can be used to examine the 3-D structure of precipitation. Several storm tops of energetic thunderstorms southwest of the weakening tropical cyclone were measured by DPR reaching heights of over 15 km (9.3 miles).
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center expects the depression to dissipate by June 30.












