
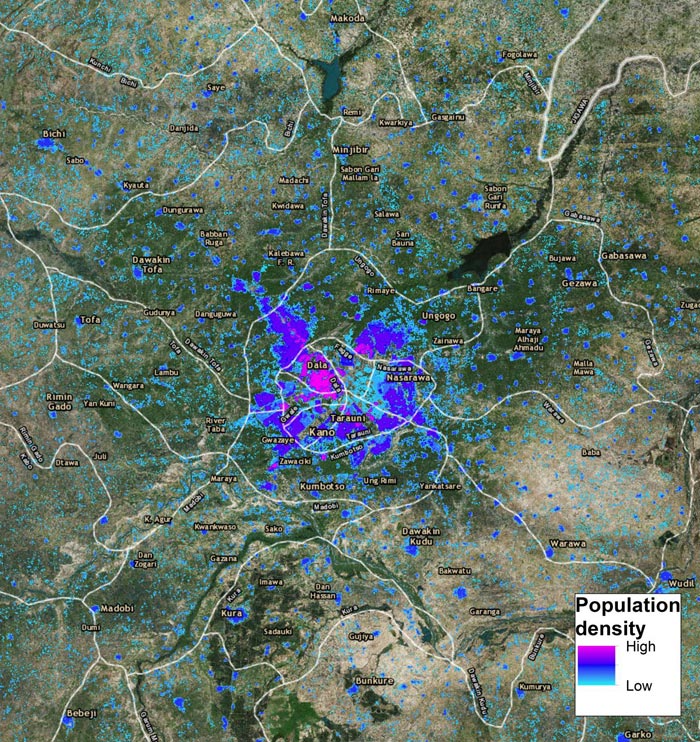
This is a map of estimates of density of children under 5 per 100 by 100m grid square, Kano city, northern Nigeria.
Credit: WorldPop
WorldPop at the University, in partnership with non-profit organisation Flowminder Foundation, is forging links with a range of countries around the globe to support the production of detailed population maps and demographic datasets which can aid governments in their efforts to develop fundamental areas such as infrastructure, healthcare and housing, and equip them effectively for disaster relief.
Understanding population numbers and distribution at local levels is crucial to national planning, but this information is often lacking in countries where no census has taken place, or census information is fragmented – perhaps due to war, political instability or poverty. For example, the most recent census conducted in Somalia was between 1985 and 1986.
Writing in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS), the researchers outline how satellite imagery, geolocation technology, small area surveys, statistical methods and computing power can come together to map high-resolution national population estimates, comparable or exceeding the level of detail of those derived from census material and with the ability to interrogate information down to the local scale.
Director of WorldPop and geographer at the University of Southampton Professor Andy Tatem explains: “These technologies provide robust data and cost-effective solutions for countries where censuses are almost impossible to conduct. Using this and other approaches, such analysis of anonymised mobile phone data, we have already been able to help combat the spread of malaria, assist in disaster relief planning following earthquakes in Nepal and Haiti and assess the potential spread of Ebola in West Africa.”
Afghanistan is another area where the researchers' work is having an impact. The country has only ever had one census, in 1979. A subsequent survey planned for 2008 was cancelled due to security concerns. Professor Tatem and his team have been working with the Afghan government and the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) to remap the country's population, and recently presented results to President Ghani in Kabul.
WorldPop's new approaches to population mapping have been boosted with a grant of $8.3M from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and the UK Government's Department for International Development. The money supports the initiation of the Geo-referenced Infrastructure and Demographic Data for Development (GRID3) program, together with UNFPA and Columbia University, aimed at supporting governments in low income countries to construct and use spatially detailed data on infrastructure and population. Most recently (7 March 2018), the GRID3 program was launched at the United Nations HQ in New York, with the aim of encouraging more governments to get involved with their research.
Professor Tatem says he'd like to replicate their previous achievements on a wider scale: “In northern Nigeria a vaccination programme focussed on eliminating polio ran out of doses in some areas because they were relying on outdated and inaccurate census data. We worked to integrate satellite mapping of settlements with ground surveys to provide more reliable estimates that are now the basis for vaccination planning. If we can duplicate similar successes across multiple countries, we can help some of the people in the world who are most in need and currently not counted.”
###
Notes to Editors
1) The work in the paper Spatially-disaggregated population estimates in the absence of national population and housing census data is supported by funding from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (OPP1134076, OPP1182408). Andrew J Tatem is supported by funding from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (OPP1106427, 1032350, OPP1117016), the Clinton Health Access Initiative, National Institutes of Health, a Wellcome Trust Sustaining Health Grant (106866/Z/15/Z), and funds from DFID and the Wellcome Trust (204613/Z/16/Z). The views expressed in the paper are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the United Nations Population Fund.
2) For more information about WorldPop, please visit: http://www.
3) For more about Flowminder Foundation visit: http://www.
4) The University of Southampton drives original thinking, turns knowledge into action and impact, and creates solutions to the world's challenges. We are among the top one per cent of institutions globally. Our academics are leaders in their fields, forging links with high-profile international businesses and organisations, and inspiring a 24,000-strong community of exceptional students, from over 135 countries worldwide. Through our high-quality education, the University helps students on a journey of discovery to realise their potential and join our global network of over 200,000 alumni. http://www.
5) Information about Geography and Environment at the University of Southampton can be found here: https:/
For interviews, please contact:
Peter Franklin, Media Relations, University of Southampton, Tel: 023 8059 5457 Email: p.franklin@southampton.ac.uk
http://www.
Follow us on twitter: http://twitter.
Like us on Facebook: http://www.















