
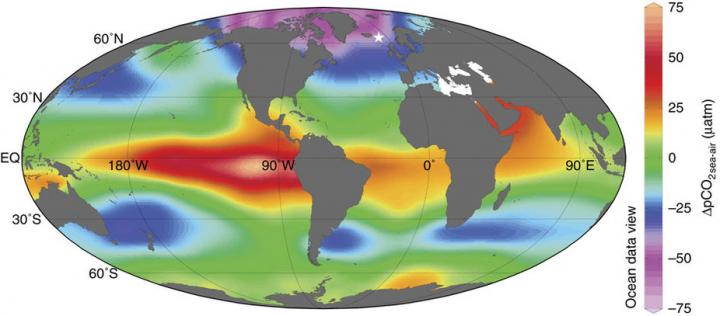
The illustration identifies the high-latitude North Atlantic as a significant CO2 sink (The purple areas are the most efficient sinks, while red ones are sources of CO2 in the modern ocean). The white star shows the location of the studied sediment core. The map was generated using data of Takahashi et al. Illustration: M. Ezat/CAGE.
Credit: Mohamed Ezat
Oceans changed function
Today the cold Arctic and Nordic Seas are especially efficient areas for uptake of CO2 from the atmosphere. (LINK) The oceans have been capable of mitigating some of the increase in greenhouse gas release resulting from human activities such as combustion of fossil fuels, by absorbing about 40% of the emitted CO2
“But our research shows that areas in Norwegian Sea on several occasions through the past 135 000 years had changed their function: instead of absorbing CO2 from the air, they released more of the greenhouse gas into it.” says first author of the study Mohamed Ezat from Centre of Arctic Gas Hydrate, Environment and Climate (CAGE), Department of Geosciences at UiT The Arctic University of Norway.
First study of its kind from the Nordic Seas
Ice cores from Antarctica show that the amount of atmospheric CO2 varied in pace with the shifting climate of ice ages and interglacial periods of the past. (LINK)
“We always thought that oceans played a major role in these shifts, as it is the largest active CO2 reservoir on this time scale. But it has remained unclear how and where in the ocean CO2 was stored and released from”, says Ezat.
Ezat and colleagues measured the boron isotopic composition of the fossil shells of near-surface dwelling, single celled organisms called foraminifera. These were collected from a marine sediment record from the Norwegian Sea spanning the last 135 000 years. This period includes two warm interglacial periods and one long-lasting ice age characterised by abrupt climate changes.
“We saw that at the end of several of the severe cooling periods in the region, so-called Heinrich events, the ocean became more acidic and later released CO2 into the atmosphere. These episodes of CO2 pumping from the Nordic Seas coincide with times of increase in atmospheric CO2.” says Ezat.
Measuring pH through thousands of years
“The variations in boron isotopes can tell us about the development in seawater pH through time and in turn give us information about the CO2 concentration in the seawater. ” explains co-author professor Tine L. Rasmussen, also from CAGE.
Doing so, the scientists were able to reconstruct the surface ocean pH and CO2 in the Norwegian Sea in relation to past climate variations, when it was warmer or colder than today. Ezat and colleagues also tried to understand why the air-sea CO2 exchange reversed in the Norwegian Sea during these times.
“We found that changes in primary productivity, input of terrestrial organic matter, and deep-water formation in the Nordic Seas, all contributed to the release of CO2 from the ocean.” says Rasmussen
Never as acidic as today
The study shows that these seas had lower pH during the episodes of CO2 release. This can however not be compared to the extent of ocean acidification that we see happening today. (LINK)
“Results of our study actually show that the sea surface pH throughout the last 135 000 years has never been as low as today in our study area. This is not an unexpected result. It is similar to previous studies conducted in other ocean areas. It does however add a body of evidence to the hypothesis that human activity is profoundly affecting the chemistry of our oceans.” Ezat says.
Scientists hope that the results will contribute to a better understanding of complex interactions between the ocean and atmosphere.
“In general, the more we learn about past changes in the Earth's climate system, the more accurate we hope we can predict the future.” says Ezat.












