
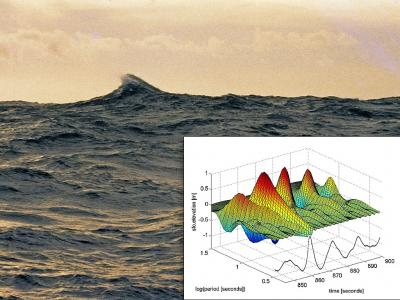
This is a rogue wave photo taken from the deck of the RV Cape Henlopen in the western North Atlantic during the Atlantic Remote Sensing Land/Ocean Experiment (ARSLOE) The crest of the rogue propogates from the right to left. Credit: H. Mitsuyasu Inset figure: Surface elevation of groups in each period band displayed on axes of time and logarithm of period in seconds. All 32 periods are displayed and their sum (divided by 20) is graphed along the time axis. The Andrea crest is at 862 s. Credit: Donelan, et.al.
Photo: H. Mitsuyasu Graph: Donelan, et.al.
University of Miami Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science scientist Mark Donelan and his Norwegian Meteorological Institute colleague captured new information about extreme waves, as one of the steepest ever recorded passed by the North Sea Ekofisk platforms in the early morning hours of Nov. 9 2007.
Within the first hour of the day, the Andrea wave passed by a four-point square array of ocean sensors designed by the researchers to measure the wavelength, direction, amplitude and frequency of waves at the ocean surface.
Using the information from the wave set–a total of 13,535 individual waves–collected by the system installed on a bridge between two offshore platforms, the researchers took the wave apart to examine how the components came together to produce such a steep wave.
The data from the 100-meter wide “wall of water” moving at 40 miles per hour showed that Andrea may have reached heights greater than the recorded height of 49 feet above mean sea level. They also found that rogue waves are not rare as previously thought and occur roughly twice daily at any given location in a storm. The findings showed that the steeper the waves are, the less frequent their occurrence, which is about every three weeks at any location for the steepest rogues.
The Andrea crest height was 1.63 times the significant height (average height of the one third highest waves). Optimal focusing of the Andrea wave showed that the crest could have been even higher and limited by breaking at 1.7 times the significant height. This establishes the greatest height rogues can reach for any given (or forecasted) significant height.
“Rogue waves are known to have caused loss of life as well as damage to ships and offshore structures,” said Mark Donelan, professor emeritus of ocean sciences at the UM Rosenstiel School. “Our results, while representing the worst-case rogue wave forecast, are new knowledge important for the design and safe operations for ships and platforms at sea.”
###
The study, titled “The Making of the Andrea Wave and other Rogues,” was published in the March 8 issue of the journal Scientific Reports. The authors include: Donelan and Anne-Karin Magnusson from the Norwegian Meteorological Institute. The work was partly performed within the ExWaMar project (ID 256466/O80) funded by the Norwegian Research Council. ConocoPhillips provided the wave data.
About the University of Miami's Rosenstiel School
The University of Miami is one of the largest private research institutions in the southeastern United States. The University's mission is to provide quality education, attract and retain outstanding students, support the faculty and their research, and build an endowment for University initiatives. Founded in the 1940's, the Rosenstiel School of Marine & Atmospheric Science has grown into one of the world's premier marine and atmospheric research institutions. Offering dynamic interdisciplinary academics, the Rosenstiel School is dedicated to helping communities to better understand the planet, participating in the establishment of environmental policies, and aiding in the improvement of society and quality of life. For more information, visit: http://www.















