
Non-Toxic Virus-Based Filament Enhances Heat Dissipation
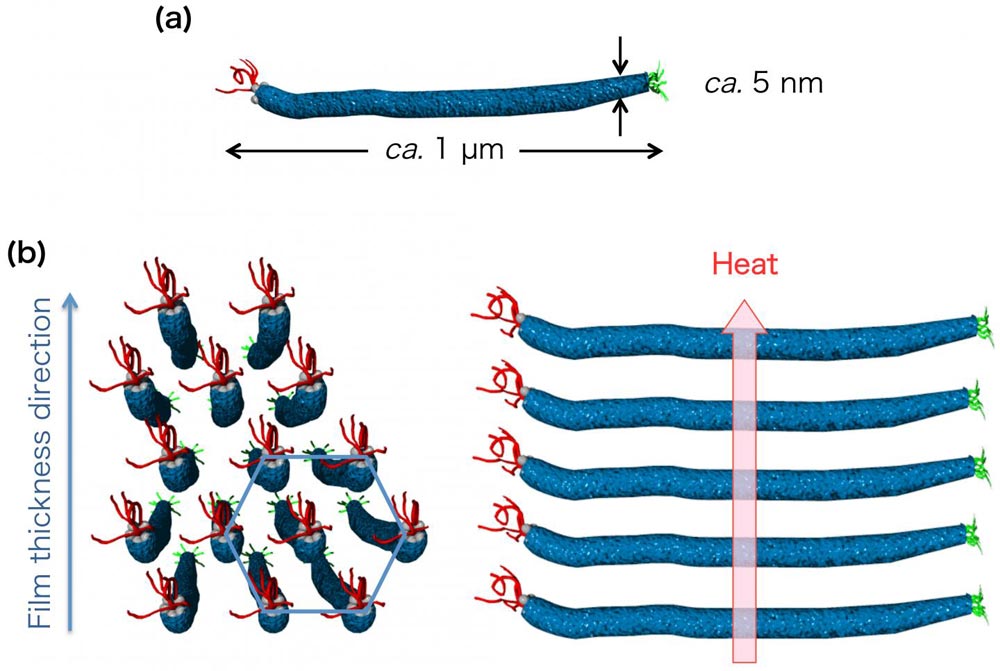
This image shows (a) phage and (b) hexagonally assembled structures of the phages in the film.
Credit: Scientific Reports
Organic polymeric materials generally have low thermal conductivity and are not suitable for rapid heat dissipation of electric and electronic equipment in the past. In order to improve its thermal conductivity, it has been considered effective to heat transfer through a covalent bond by “orientation processing” in which molecules are aligned in the same direction, or to composite with an inorganic material.
A research team led by Assistant Professor Toshiki Sawada and Professor Takeshi Serizawa is focusing on the capability to form regularly assembled structures in a wide scale from nano to macro (so called hierarchical assembly[1]) observed in the natural systems and the hierarchically assembled structures prepared in this way, the phenomenon where molecules accumulate around the perimeter as an aqueous solution in which molecules are dissolved evaporates (coffee ring effect[2]) was utilized to assemble a filamentous virus for the film preparation.
As a result, it was found that the thermal diffusivity at the edge of the film drastically enhanced to a value comparable to that of inorganic glass, and that facilitates the utilization of the hierarchically assembled biomacromolecule[3]. This helps future development of electric and electronic devices composed of not only viruses but also various naturally derived molecules.
Until now, orientation processing and compositing with inorganic materials have been considered effective for the high thermal conductivity of organic polymeric materials. However, since this virus film can be prepared by evaporating an aqueous solution of a filamentous virus at room temperature, it is expected to lead to the establishment of a method for easily constructing heat dissipation materials under mild conditions that do not require special operations.
###
The achievements of this research are supported by the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) through the Precursory Research for Embryonic Science and Technology (PRESTO) “Nanoscale Thermodynamics-based Development of Innovative Materials for Energy Transport Using Hierarchically Assembled Biomacromolecules” in the Strategic Basic Research Programs “Thermal Science and Control of Spectral Energy Transport”, and the results will be published in the British science journal Scientific Reports (Online) on April 3, 2018.
[Explanations of Technical Terms]
[1] Hierarchical assembly: Regularly assembled structure in a wide scale such as molecular scale (nanometer) to macro scale (millimeter).
[2] Coffee ring effect: When droplets of spilled coffee evaporate, the perimeter of the droplet evaporates quickly, causing the phenomenon where coffee particles gather at the perimeter of the droplet.
[3] Biomacromolecules: Polymers observed in natural systems. Polymeric biomolecules.












