
Ballet Bugs: Nature’s Blueprint for Better Robot Design
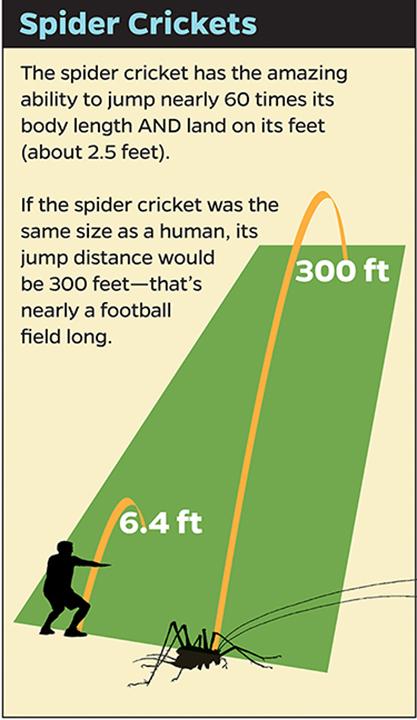
If spider crickets were as large as humans, how far could they jump?
Credit: Royce Faddis/Johns Hopkins University
When it's time to design new robots, sometimes the best inspiration can come from Mother Nature. Take, for example, her creepy, but incredibly athletic spider crickets.
Johns Hopkins engineering students and their professor have spent more than eight months unraveling the hopping skills, airborne antics and safe-landing patterns of these pesky insects that commonly lurk in the dark corners of damp basements.
The team, which hopes to pave the way for a new generation of small but skillful jumping robots, will present its findings Nov. 23 during a poster session in Boston at the 68th annual meeting of the American Physical Society's Division of Fluid Dynamics.
Caption: Undergraduate researcher Emily Palmer and one of her spider cricket subjects. (Credit: Will Kirk/Johns Hopkins University)
The Johns Hopkins team members believe non-human creatures may be the best models in designing mechanical helpers to carry out certain important tasks. Figuring out how critters move, they say, could lead to planetary rovers that crawl like caterpillars or winged drones that hover like hummingbirds.
So what design tips did the researchers manage to glean from these spindly six-legged bugs?
For one thing, the Johns Hopkins researchers were able to use high-speed video cameras to collect tantalizing clues about how these tiny wingless creatures can somehow leap a distance equal to about 60 times their body length. That's a feat far beyond what any human track star could accomplish. An adult human who wanted to replicate the cricket's leap would have to jump 300 feet or more–roughly the length of a football field. And, most times, spider crickets manage to land safely on their feet. How, the researchers wanted to know, can these tiny bugs accomplish this?
“Because they don't have wings, the main things they use during their 'flight' to stabilize their posture is their limbs,” said Emily Palmer, a sophomore mechanical engineering major in the university's Whiting School of Engineering who is doing much of the testing. “We're looking at the way the spider crickets move their bodies and move their limbs to stabilize their posture during a jump.”
And why would such knowledge be useful?
“Ultimately, the application would be in really tiny robots,” said Palmer, who is from Exeter, N.H. Deploying tiny high-jumping robots to travel over rugged, uneven ground, she said, would utilize a more efficient and probably less expensive form of locomotion, compared to flying robots or humans on foot.
To get a clear, close-up view of the crickets' limber limbs in action, the team's three video cameras each snap 400 frames per second. Then, by slowing down the finished footage, the researchers see precisely how each spindly insect leg contributed to the amazing leaps and landings.
Rajat Mittal, the Johns Hopkins mechanical engineering professor who is supervising the research, was startled to see that, in slow-motion, the crickets' limb movements bore an uncanny resemblance to classical dance.
“These videos have actually been quite eye-opening,” he said, “because it's only when you slow these critters down that you really start to see the beauty and the intricacy of their movement. The analogy that comes to mind is of a ballerina performing a ballet. It's a very beautiful, controlled, intricate motion.”
But Mittal and his students found that beneath such artistic movements lie some serious lessons in aerodynamics. The slow-motion playback confirmed that during the “flight” segment of their jumps, the crickets carefully use their limbs and even perhaps their antennae to stabilize their posture and prepare for a safe landing. The crickets seek to land on their feet, the researchers said, so that they can quickly be prepared to leap again to escape any predators that are waiting to pounce.
Some of the video footage yielded surprises. The team discovered that as the crickets soared upward during the early part of their jumps, the bugs streamlined their bodies like a projectile to maximize the distance they would travel. “They really are masters of aerodynamics,” Mittal said.
Captured by the lab's cameras, this aerial mastery was transferred to computers to create detailed three-dimensional models depicting how each insect's body parts move during a leap and a touchdown. Mittal suggested that a new generation of jumping micro-robots modeled on these crickets might someday be able to help look for victims after a powerful earthquake or carry out other tasks without putting humans searchers at risk.
###
Other participants in this research project were Noah Cowan, a Johns Hopkins associate professor of mechanical engineering; David Gorman and Catarina Neves, both Johns Hopkins undergraduate seniors majoring in mechanical engineering; and Nicolas Deshler, a high school intern who is currently in his senior year at Washington International School in Washington, D.C. Deshler's participation was supported by the Research Experience for Undergraduates Program, funded by the National Science Foundation and administered at Johns Hopkins by the university's Institute for NanoBioTechnology.
Video footage, still photos and an info graphic are available; contact Phil Sneiderman.












