
VTT Unveils New Technique for Energy Harvesting from Vibrations
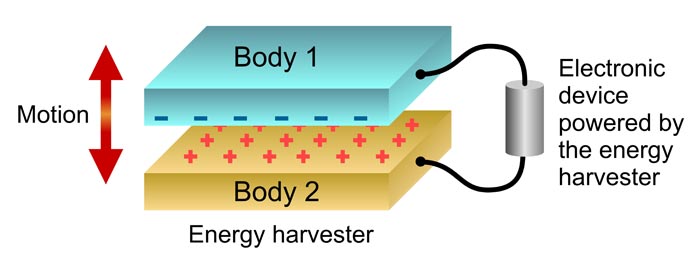
Schematic of the new electricity generation technique. Bodies 1 and 2 have different work functions.
The new method can be used in harvesting energy from mechanical vibrations of the environment and converting it into electricity. Energy harvesters are needed, for example, in wireless self-powered sensors and medical implants, where they could ultimately replace batteries.
In the future, energy harvesters can open up new opportunities in many application areas such as wearable electronics.
Research scientists at VTT have successfully generated energy by utilizing the charging phenomenon that occurs naturally between two bodies with different work functions. Work function is the amount of energy needed to remove an electron from a solid and it determines, for example, the well-known photoelectric effect.
When two conducting bodies with different work functions are connected to each other electrically, they accumulate opposite charges. Moving of these bodies with respect to each other generates energy because of the attractive electrostatic force between the opposite charges.
In VTT’s experiment the energy generated by this motion was converted into useful electrical power by connecting the bodies to an external circuit. This new energy conversion technique also works with semiconductors.
In many sensor applications and medical implants such as pacemakers, electricity is typically provided by batteries. Research into small energy harvesters that turn mechanical vibration into electricity has focused on piezoelectric and electrostatic devices. Unlike these devices VTT’s technique does not require an integrated battery, electrets or piezo materials.
VTT estimates that the new electricity generation technology could be introduced on an industrial scale within three to six years. Energy harvesters and new sensing solutions are among the projected megatrends of the near future. Energy harvesters can replace batteries and other energy sources in applications where maintenance is difficult or impossible.
The findings of the study were published in the Scientific Reports online journal.
The full article can be read at http://www.nature.com/srep/2014/141028/srep06799/full/srep06799.html
Aapo Varpula
Research Scientist
+358 20 722 4278
Mika Prunnila
Chief Research Scientist, Team Leader
+358 20 722 6668












