
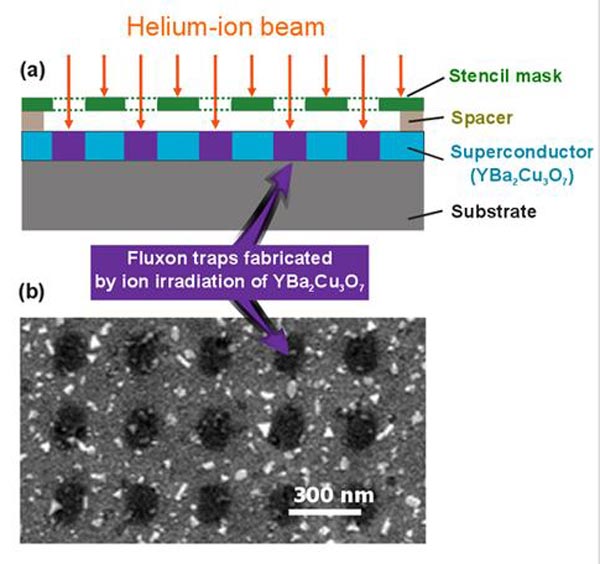
The principle of the fabrication of a "quantum egg-box" with a novel masked ion-beam technology. It allows to produce at the same time hundreds of thousands of traps for fluxons.
Copyright: Wolfgang Lang, University of Vienna
Speeding up data processing in computers goes hand in hand with a greater heat generation, which limits the performance of fast computers. Researchers have therefore long been trying to develop digital circuits based on superconductors – those puzzling materials that can transport electricity completely without loss when cooled below a certain critical temperature.
Magnetic quantum objects in superconductors
Inside a superconductor, a magnetic field can exist only in small quantized pieces, the fluxons. These are particularly suitable for the storage and processing of data bits. In a homogeneous superconductor, the fluxons are arranged in a hexagonal lattice. Using modern nanotechnology, researchers at the University of Vienna and the Johannes-Kepler-University Linz have now succeeded in building artificial traps for fluxons. By means of these traps the fluxons are forced into a predefined formation.
The importance of the non-equilibrium
Until now, the fluxons could only be observed in a thermodynamic equilibrium, i.e., in a uniform arrangement. “If we try to stack two eggs on top of each other in an egg-box and leave the adjacent pit empty, the egg would quickly roll down and we end up in the equilibrium state with exactly one egg in each pit,” explains Wolfgang Lang from the University of Vienna.
From the viewpoint of data processing, however, the fully-filled egg-box contains little information and is therefore useless. It would be much more useful to place the eggs in a predefined pattern. In such a way, for example, the QR code, recognized by smartphones, could be realized in an egg-box – obviously a large amount of information.
At the nanoscale, the researchers have now made a major step forward in this direction by demonstrating for the first time a stable non-equilibrium state of fluxons in an array of more than 180,000 artificial traps.
Depending on the external magnetic field, the fluxons arrange themselves in terraced zones, in which each trap either captures no fluxon, exactly one, or even several fluxons. “Even after days, we have observed precisely the same arrangement of fluxons – a long-term stability that is rather surprising for a quantum system,” says Georg Zechner of the University of Vienna, the lead author of the study.
Nanopatterning of superconductors by ion beams
These research results were enabled by a new method, developed by the physicists in Linz and Vienna together with the Vienna-based high-tech company IMS Nanofabrication AG. “Masked ion-beam irradiation allows for the fabrication of nanostructures in superconductors in a single step. It can be applied time-efficiently to large areas, can be ramped-up to an industrial scale and does not require any chemical processes,” emphasizes Johannes D. Pedarnig of the Institute of Applied Physics at the Johannes-Kepler-University Linz.
Depending on the mask used, virtually any desired structure can be patterned into the superconductor. The scientists are now planning further experiments on more sophisticated nanostructures, which should demonstrate the systematic transfer of fluxons from one trap to the next. This could be another pioneering step towards the development of fast computer circuits based on fluxons.
Publication in “Physical Review Applied”
“Hysteretic vortex matching effects in high-Tc superconductors with nanoscale periodic pinning landscapes fabricated by He ion beam projection technique”:
G. Zechner, F. Jausner, L. T. Haag, W. Lang, M. Dosmailov, M. A. Bodea, J. D. Pedarnig
Phys. Rev. Applied 8, 014021, 21 July 2017
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.8.014021
https://journals.aps.org/prapplied/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevApplied.8.014021
Scientific contact
ao. Univ.-Prof. Dr. Wolfgang Lang
Electronic Properties of Materials
Faculty of Physics
University of Vienna
1090 Vienna, Boltzmanngasse 5
M +43-664-602 77-514 24
wolfgang.lang(at)univie.ac.at
http://epm.univie.ac.at/
Press contact
Mag. Alexandra Frey
Press office, University of Vienna
Research and Teaching
1010 Vienna, Universitätsring 1
T +43-1-4277-175 33
M +43-664-602 77-175 33
alexandra.frey@univie.ac.at












