
Enhancing Data Storage: Skyrmions Improve Magnetic Bit Stability
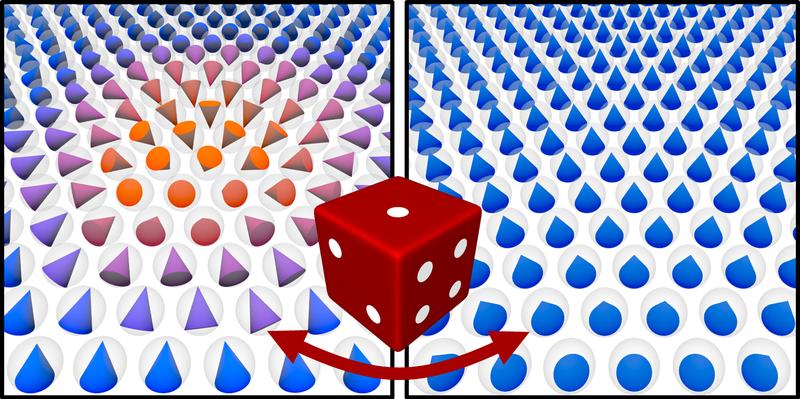
The configurations of a magnetic skyrmion on the left side and of a ferromagnet on the right side. The cones indicate the orientations of the localized atomic magnets. The skyrmion consists of a small number of atoms only and has a diameter of a few nanometers. Researchers of the University of Hamburg studied the spontaneous switching between the two states which may be the bits of information in future data storage devices.
(Image: J. Hagemeister, University of Hamburg)
One of the cogent necessities in the contemporary world is the storage of a vast amount of digital data. Currently, there are different methods available for that purpose including the use of differently magnetized ferromagnetic cells.
All atomic magnets are aligned parallel within these cells and can in principle point into two different directions. Thereby, each cell may be in either one of two different states and thus provides the elementary building block of a digital data storage device.
The arrangement of a large number of these cells can be found on a magnetic disc of a conventional hard drive.
In order to be able to meet the demands for data storage devices with even higher capacities in the future, the density of the data storage cells needs to be increased. This process is limited for the current magnetic storage devices, since there is a minimal cell size for stable magnetic bits. Cells become thermally unstable below this critical size and spontaneously change their state resulting in a loss of the stored information.
Therefore, new concepts for storage devices are required and in this context, especially the discovery of magnetic skyrmions in ultrathin metallic films has gained considerable attention in recent years. A skyrmion is a magnetic knot in which the magnetization distribution is twisted.
These skyrmion knots are very stable objects and therefore offer great potential for ultra-dense magnetic data storage. The information would be stored in the skyrmion (“1”) and the ferromagnetic state (“0”).
As the interdisciplinary journal „Nature Communications“ reports on the 14th of October, scientists of the University of Hamburg investigated for the first time the stability of single skyrmions as a function of temperature and a stabilizing external magnetic field.
The lifetime of the skyrmion could be adjusted by a variation of the magnetic field strength. The work has demonstrated that the two states “0” (ferromagnet) and “1” (skyrmion) are very different from each other not only in the magnetic configuration but also in their stability properties.
“Our investigations have shown that skyrmion knots can only be erased with effort from a ferromagnetic surface. This makes them valuable for the application in future data storage devices.” says Dr. Elena Vedmedenko from the research group of Prof. Roland Wiesendanger.
The results will contribute to tailor the lifetimes of magnetic skyrmions in future skyrmion-based memory and logic devices.
Further information:
Heiko Fuchs
Sonderforschungsbereich 668
Universität Hamburg
Jungiusstr. 9A, 20355 Hamburg, Germany
phone.: +49 40 4 28 38 – 69 59
fax: +49 40 4 28 38 – 24 09
e-mail: hfuchs@physnet.uni-hamburg.de
http://www.sfb668.de
http://www.nanoscience.de












