
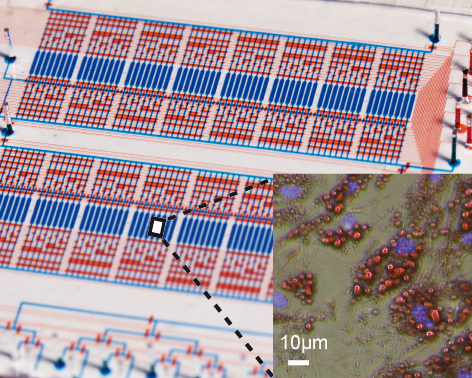
Caption: The microfluidic chip (background) and adipose cells (close-up section view).
Source: Matthias Meier
A Freiburg-based research group has developed a microfluidic chip where more than one hundred apidose-derived adult stem cell cultures can grow and divide. In the human body, adipose tissue acts as a primary energy store.
Adult stem cells have the task of maintaining and regenerating this process. The researchers used the new lab-on-a-chip to study how adult stem cells in adipose tissue develop into mature fat cells, conducting their investigations outside the body. Previous experiments have enabled them to decode a signalling pathway involved in adipose cell maturation and to show that calories in the nutrient medium influence this process.
The team has published the results of its research in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). “Going forward, we want to investigate the environmental factors – particularly the nutrient conditions – that cause different adipose cell types to grow,” explains biophysicist Dr. Matthias Meier. “This will enable us to develop new approaches to combating obesity and diabetes.”
In contrast to embryonic stem cells, when adult stem cells divide, their offspring are only able to develop at the same site and in certain tissue types. Factors such as insulin and blood sugar levels also influence whether or not adult stem cells in adipose tissue will develop into mature adipose cell. Aberrations in this maturation process can lead to diabetes or obesity. The multitude of factors operating here make it very complicated, however, for scientists to investigate this process outside the body.
In order to overcome this problem, the Freiburg-based research group has developed a microfluidic chip that works with minute volumes of liquid: The platform uses microchannels to feed cell cultures with nutrients during their three-week growth period. A special feature of the set-up is an automatic protein analysis program integrated into the chip, which decodes signalling pathways during cell growth.
The new technology allows the researchers to vary the external cell factors such that the micro-environment on the chip resembles conditions within the body as closely as possible. This enabled adipose-derived adult stem cells to be successfully converted into mature fat cells within the experiments, and the corresponding signalling pathway mTORC1 was also decoded. “By increasing the calorie content in the nutrient medium, we were able to show that fat is stored more rapidly during maturation,” states Meier.
“However, it remains unclear whether adjusting the calorie levels in this way leads to an increased rate of adipose cell formation.” To answer this question, the research team now wants to systematically use the chip technology to study the association between human eating habits and the formation of fat cells.
Eight researchers were involved in the study: Matthias Blazek, Matthias Meier, Indranil Mitra, Alina Platen, Nils Schneider, Xuanye Wu and Prof. Dr. Roland Zengerle conduct research at the Department of Microsystems Engineering (IMTEK) and belong to the BIOSS Centre for Biological Signalling Studies Cluster of Excellence at the University of Freiburg. Prof. Dr. Roland Schüle is the Scientific Director of the Centre for Clinical Research at Freiburg University Hospital.
Original publication:
Xuanye Wu, Nils Schneider, Alina Platen, Indranil Mitra, Matthias Blazek, Roland Zengerle, Roland Schüle and Matthias Meier (2016). In situ characterization of the mTORC1 during adipogenesis of human adult stem cells on chip. PNAS Early Edition. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1601207113
Contact:
Dr. Matthias Meier
Institut für Mikrosystemtechnik
Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg
Phone: +49 (0)761 / 203 – 73241
E-Mail: matthias.meier@imtek.uni-freiburg.de















