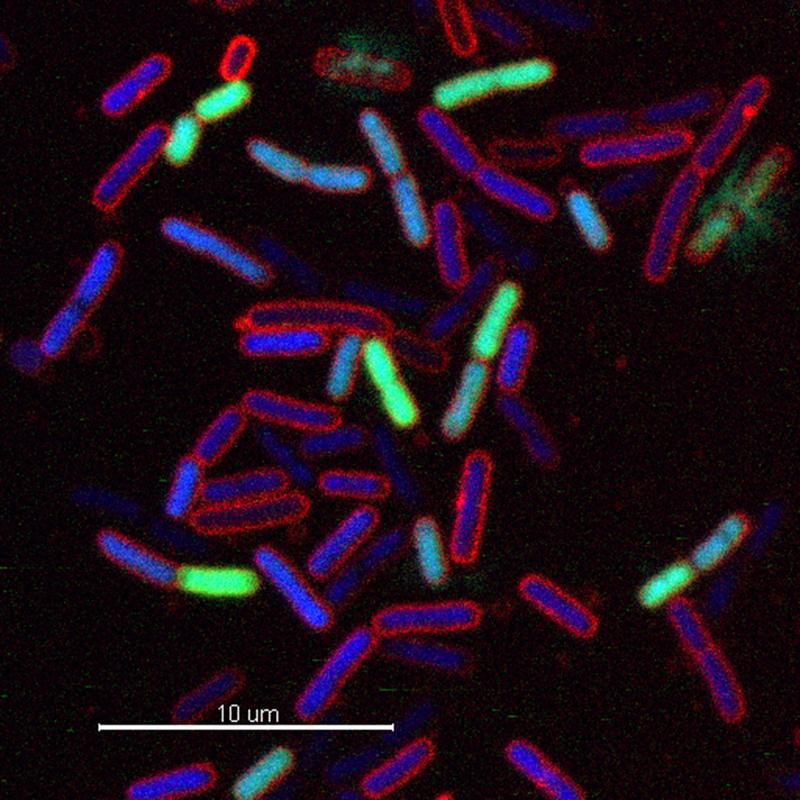
Escherichia coli cells treated with a novel chimeric peptidomimetic antibiotic. Cells in blue are alive while green cells are already killed by the antibiotic (cell lysis).
Matthias Urfer, UZH
The rapid emergence of antimicrobial resistance is a matter of global concern. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), particularly Gram-negative bacteria like Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacteriaceae that are resistant to the carbapenem and cephalosporin antibiotics, pose a growing threat to human health.
These pathogens can cause severe and often life-threatening infections. The last new class of antibiotics to reach the market against these microorganisms, the fluoroquinolones, dates back to the 1960s.
Novel antibiotics with new mechanisms of action against Gram-negative bacteria are urgently needed, especially because resistance against the last resort antibiotic colistin is on a global rise.
Novel family of antibiotics against dangerous bacteria
Swiss research teams headed by the University of Zurich (UZH) and Polyphor AG now report the discovery and characterization of a new family of synthetic antibiotics that possess broad-spectrum anti-Gram-negative antimicrobial activity.
“The new antibiotics interact with essential outer membrane proteins in Gram-negative bacteria”, says John Robinson from the UZH Department of Chemistry, who co-headed the study.
“According to our results, the antibiotics bind to complex fat-like substances called lipopolysaccharides and to BamA, an essential protein of the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria”, Robinson adds.
Disruption of outer membrane synthesis via unexploited mechanism of action
BamA is the main component of the so-called ß-barrel folding complex (BAM), which is essential for outer membrane synthesis. After targeting this essential outer membrane protein, the antibiotics destroy the integrity of the bacterial membranes and the cells burst.
The outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria has the important function to protect the cells from toxic environmental factors, such as antibiotics. It is also responsible for the uptake and export of nutrients and signaling molecules. “Despite its critical importance, so far no clinical antibiotics target these key proteins required for outer membrane biogenesis”, Robinson says.
Lead molecule in preclinical studies
The research was carried out in close collaboration with Polyphor AG, a former UZH start-up company that was founded in 1996. The clinical stage biopharmaceutical company based in Allschwil now plans to progress one compound into human clinical trials. “POL7306, a first lead molecule of the novel antibiotics class, is now in preclinical development”, says Daniel Obrecht, chief scientific officer at Polyphor and co-head of the work.
National Research Programme “Antimicrobial Resistance” (NRP 72)
This study published in “Nature” was done by the University of Zurich and Polyphor AG, along with interdisciplinary groups in the University of Basel and the ETH Zurich. The work also falls within the framework of the National Research Programme “Antimicrobial Resistance” (NRP 72). It is part of the project “The molecular mechanism of outer membrane protein insertion by BamA and its role as a target for new antibiotics” headed by Prof. Sebastian Hiller from the Biozentrum of the University of Basel.
More information: www.nrp72.ch
Prof. em. Dr. John A. Robinson
Department of Chemistry
University of Zurich
Phone: +41 79 438 23 33
E-mail: john.robinson@chem.uzh.ch
Anatol Luther et. al. Chimeric Peptidomimetic Antibiotics Against Gram-Negative Bacteria. Nature. 23 October 2019. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1665-6