
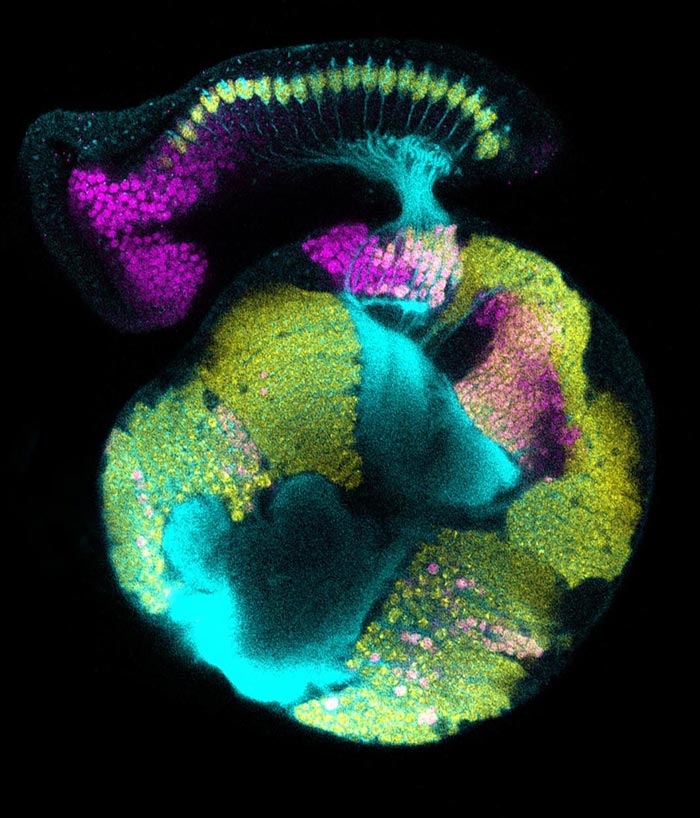
A confocal micrograph of a developing fruit fly visual system. Development of the retina (top) is coordinated with development of the optic lobe region of the brain (sphere below). All neurons are marked by yellow and their axon projections in cyan; magenta in the optic lobe marks the specific region of the brain where neuronal differentiation is regulated by glia.
Courtesy of Vilaiwan M Fernandes, Desplan Lab, NYU's Department of Biology
The research, which appears in the journal Science, discovered that glia, a collection of non-neuronal cells that had long been regarded as passive support cells, in fact are vital to nerve-cell development in the brain.
“The results lead us to revise the often neuro-centric view of brain development to now appreciate the contributions for non-neuronal cells such as glia,” explains Vilaiwan Fernandes, a postdoctoral fellow in New York University's Department of Biology and the study's lead author.
“Indeed, our study found that fundamental questions in brain development with regard to the timing, identity, and coordination of nerve cell birth can only be understood when the glial contribution is accounted for.”
The brain is made up of two broad cell types, nerve cells or neurons and glia, which are non-nerve cells that make up more than half the volume of the brain. Neurobiologists have tended to focus on the former because these are the cells that form networks that process information.
However, given the preponderance of glia in the brain's cellular make-up, the NYU researchers hypothesized that they could play a fundamental part in brain development.
To explore this, they examined the visual system of the fruit fly. The species serves as a powerful model organism for this line of study because its visual system, like the one in humans, holds repeated mini-circuits that detect and process light over the entire visual field.
This dynamic is of particular interest to scientists because, as the brain develops, it must coordinate the increase of neurons in the retina with other neurons in distant regions of the brain.
In their study, the NYU researchers found that the coordination of nerve-cell development is achieved through a population of glia, which relay cues from the retina to the brain to make cells in the brain become nerve cells.
“By acting as a signaling intermediary, glia exert precise control over not only when and where a neuron is born, but also the type of neuron it will develop into,” notes NYU Biology Professor Claude Desplan, the paper's senior author.
###
For a time-lapse movie of a fruit fly visual system developing over the course of six hours, please click here: http://bit.
The research was supported, in part, by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (EY13012).












