
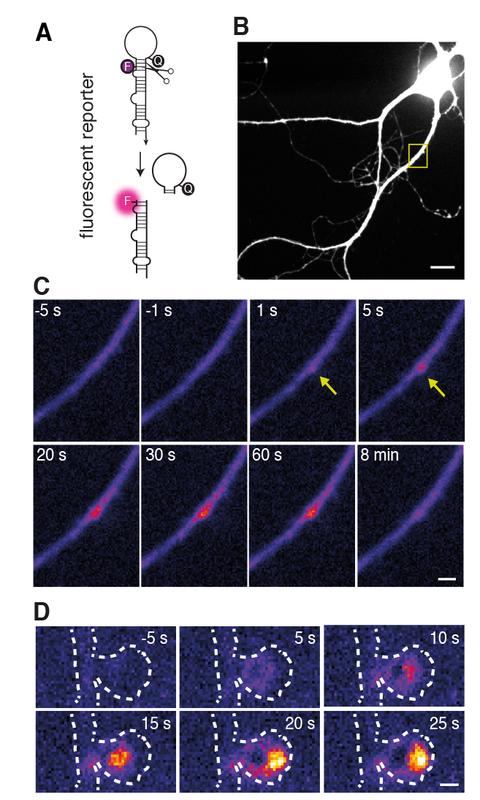
Scheme of the fluorescent molecular reporter (A), an individual reporter in a brain cell and microRNA birth in the dendrites (C) as well as within an individual synapse (D)
Max Planck Institute for Brain Research
Proteins are the building blocks of all cells. They are made from messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules, which are copied from DNA in the nuclei of cells. All cells, including brain cells, called neurons, carry out their functions by carefully regulating the amount and kind of proteins they make.
An important feature of neurons is their ability to communicate with one another at synapses, the points of contact between two cells. Synapses use proteins that are synthesized close-by to fuel communication and the formation of memories.
In neurons and other cells, protein synthesis is regulated by microRNAs, very small “non-coding” RNAs that bind, using complementary sequences, to mRNA and prevent the mRNA from being made into protein. microRNAs are made from larger precursor RNA molecules by several processing steps in the nucleus and cytoplasm.
In individual cells, copy numbers of most microRNAs in single cells are relatively low in contrast to potential mRNA targets within individual cells where copy numbers can be up to 10,000 molecules. As such, the absolute number of potential mRNA targets within a cell for a single microRNA species could be very high (e.g. millions), raising the question of how a microRNA can effectively regulate a particular target mRNA.
In the February 10th issue of Science, the Schuman and Heckel labs, from the Max Planck Institute for Brain Research and Goethe University, respectively, show that neurons have solved the abundance problem by moving the site of microRNA maturation (or “birth”) away from the cytoplasm out to the dendrites, thin processes, which are closer to where synapses are. This puts the newly born microRNA into much smaller environment with fewer mRNA target options.
“We tested this hypothesis by using a clever design of a fluorescent molecular reporter, modelled after an immature microRNA”, Heckel says. “We filled neurons with this probe and then stimulated individual synapses. To our surprise, we could then see bright fluorescent spots at the stimulated synapses, showing us the birth of the microRNA. We then saw that the microRNA target was downregulated in the neighborhood of the dendrite where the microRNA was born.”.
Schuman: “By moving the birthplace of the microRNA to the dendrites and synapses where it is closer to its targets, neurons have solved the microRNA-mRNA numbers game and gained a way for external events-resulting in the activation of synapses, to control the local expression of important brain molecules which is important for neuronal communication and also for memory formation.”












