Building a brain, cell by cell: Researchers make a mini neuron network (of two)
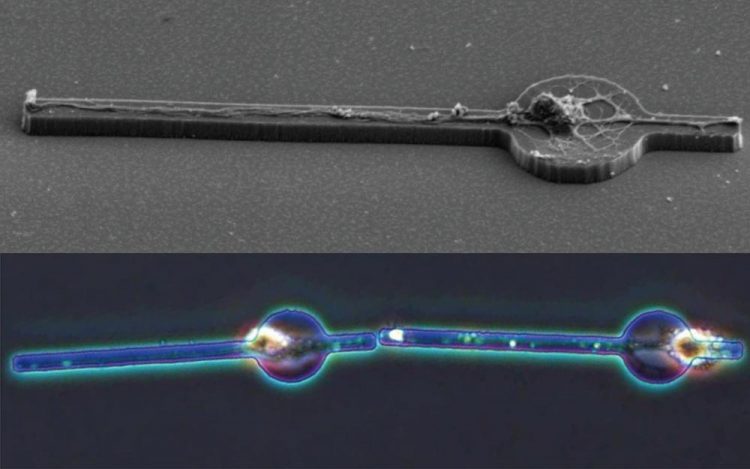
A single neuron on a microplate (SEM image) and two adjoining neurons that were physically connected. Credit: 2018 Shoji Takeuchi, Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo
In a report published in Micromachines, researchers at The University of Tokyo Institute of Industrial Science describe their new method to create one such model, using microscopic plates to connect neurons together one cell at a time.
Research into the brain typically involves the use of in vitro cultures, which are collections of neurons grown together in a dish.
A culture represents, in effect, a highly pared-down version of a brain, and one that can be chemically or electrically manipulated. While cultures are indispensable to neurological research, they suffer from considerable limitations.
“In vitro culture models are essential tools because they approximate relatively simple neuron networks and are experimentally controllable,” study first author Shotaro Yoshida explains.
“These models have been instrumental to the field for decades. The problem is that they're very difficult to control, since the neurons tend to make random connections with each other. If we can find methods to synthesize neuron networks in a more controlled fashion, it would likely spur major advances in our understanding of the brain.”
The researchers took advantage of recent insights into how neurons behave; namely, that geometric shapes can help guide neurons, telling them where and how to grow. In this case, the team used a synthetic neuron-adhesive material to make a microscopic plate.
The plate is circular with two protruding rectangles, somewhat resembling a bead on a tight string. They found that this shape guides neurons to grow in a very defined way: when placed onto the microplate, a neuron's cell body settles onto the circle, while the axon and dendrites – the branches that let neurons communicate with each other – grow lengthwise along the rectangles.
“What was especially important in this system was to have control over how the neurons connected,” Yoshida adds. “We designed the microplates to be movable, so that by pushing them around, we could physically move two neurons right next to each other. Once we placed them together, we could then test whether the neurons were able to transmit a signal.”
Neurons communicate with one another through synapses, specialized structures that let chemical messengers travel from one neuron to the next. Using a technique to visualize the parts of a synapse, the research team found that the microplate-riding neurons were indeed able to form these communication hubs. What was more, the hubs were functional: when one neuron lit up with electrically charged ions, its partner lit up at precisely the same time.
While the team aims to further refine the system (only a small fraction of neurons could be successfully connected through working synapses), the results of the study suggest an important step forward in using microplates for research.
“This is, to the best of our knowledge, the first time a mobile microplate has been used to morphologically influence neurons and form functional connections,” lead investigator Shoji Takeuchi concludes. “We believe the technique will eventually allow us to design simple neuron network models with single-cell resolution. It's an exciting prospect, as it opens many new avenues of research that aren't possible with our current suite of experimental tools.”
###
The article, “Assembly and Connection of Micropatterned Single Neurons for Neuronal Network Formation,” was published in Micromachines at DOI: 10.3390/mi9050235.
About Institute of Industrial Science (IIS), the University of Tokyo
Institute of Industrial Science (IIS), the University of Tokyo is one of the largest university-attached research institutes in Japan.
More than 120 research laboratories, each headed by a faculty member, comprise IIS, with more than 1,000 members including approximately 300 staff and 700 students actively engaged in education and research. Our activities cover almost all the areas of engineering disciplines. Since its foundation in 1949, IIS has worked to bridge the huge gaps that exist between academic disciplines and real-world applications.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

New organoid with all key pancreas cells
Researchers from the Organoid group (previously Clevers group) at the Hubrecht Institute have developed a new organoid that mimics the human fetal pancreas, offering a clearer view of its early development….

Unlocking the potential of nickel
New study reveals how to use single atoms to turn CO2 into valuable chemical resources. Nickel and nitrogen co-doped carbon (Ni-N-C) catalysts have shown exceptional performance in converting CO2 into…

‘Spooky action’ at a very short distance
Scientists map out quantum entanglement in protons. Particles streaming from collisions offer insight into dynamic interactions and collective behavior of quarks and gluons. Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s…



