
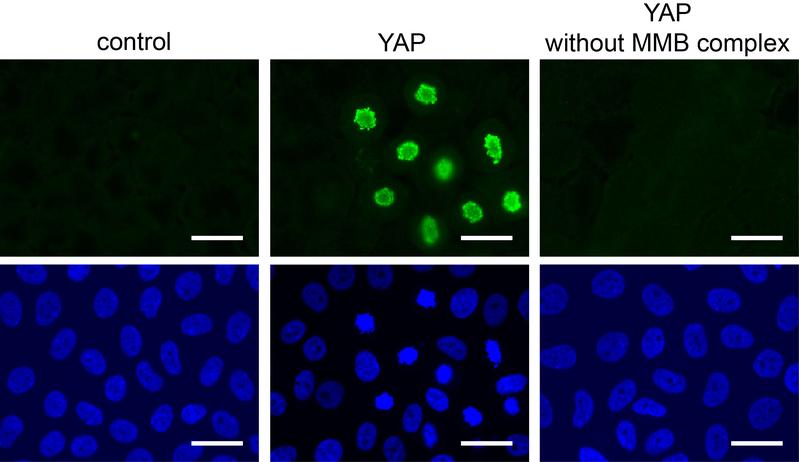
Cells divide after activation of YAP (green staining) – but only if the MMB protein complex is intact.
Image: AG Gaubatz / University of Wuerzburg
In malignant tumours, the cells usually proliferate quickly and uncontrollably. A research team from the Biocenter of Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) Würzburg in Bavaria, Germany, has discovered that two important regulators of cell division can interact in this process.
If this is the case, affected patients have particularly poor chances of survival. A special form of lung cancer was investigated.
The JMU team led by Professor Stefan Gaubatz and Dr. Grit Pattschull from the Chair of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology II analysed the activities of the protein YAP and the protein complex MMB (Myb-MuvB).
According to the researchers, the former protein is only able to initiate cell division when it interacts with a subunit of the MMB complex. The molecular details of these processes are currently described in the journal Cell Reports.
“Our results show for the first time that there is a connection between these two cancer-relevant signalling pathways,” said Professor Gaubatz. If this connection can be broken, this could possibly be applied for cancer therapy.
Next, the JMU research team will investigate the exact details of the interaction between YAP and the MMB protein complex. In particular, the researchers hope to identify further proteins that are involved in the interaction of the two signalling pathways. The long-term goal is to suppress tumour growth by blocking the interaction.
This work was financially supported by the German Cancer Aid, among others.
Prof. Dr. Stefan Gaubatz, Biocenter of the University of Würzburg, T +49 931 31-84138, stefan.gaubatz@biozentrum.uni-wuerzburg.de
Pattschull, Grit et al.: “The Myb-MuvB complex is required for YAP-dependent transcription of mitotic genes”, Cell Reports, 18 June 2019, DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.05.071












