Chains of nanogold – forged with atomic precision
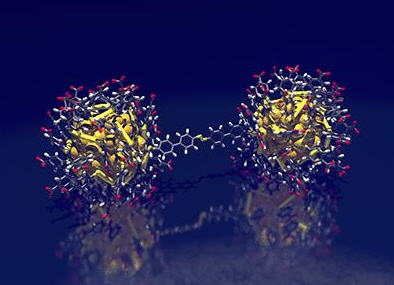
Nanotechnology gives us tools to fabricate nanometer sized particles where only a few hundred metal atoms form their core. New interesting properties emerge in this scale, for example, the light–matter interaction is extremely strong and catalytic activity increased. These properties have led to several applications, such as, chemical sensors and catalysts.
“Synthesis of nanoparticles usually yields a variety of sizes and shapes”, say lecturer Dr Tanja Lahtinen. The approach we use is exceptional in the sense that after purification we get only a single type of a nanoparticle. These nanoparticles have a specified number of each atom and the atoms are organized as a well-defined structure. It is essentially a single huge molecule with a core of gold. These nanoparticles were linked with molecular bridges forming pairs, chains, and rings of nanoparticles.
“When these kind of nanostructures interact with light, electron clouds of the neighboring metal cores become coupled”, explains researcher Dr Eero Hulkko. The coupling alters significantly the electric field what molecules in between the particles feel.
“Studying nanostructures that are well-defined at the atomic level allows us to combine experimental and computational methods in a seemless way”, continues Dr Lauri Lehtovaara, Research Fellow of the Finnish Academy. We are aiming to understand light–matter interaction in linked metallic nanostructures at the quantum level. Deeper understanding is essential for development of novel plasmonic applications.
The research continues a long-term multidispilinary collaboration at Nanoscience Center of University of Jyväskylä.
“I am very happy that our dedicated efforts on studying monolayer protected clusters and their applications have created an unique multidisiplinary center of excellence which is able to continuously publish high impact science”, says Hannu Häkkinen, an Academy Professor and head of the Nanoscience Center.
In addition to the above persons, Karolina Sokołowska, Dr Tiia-Riikka Tero, Ville Saarnio, Dr Johan Lindgren, and Prof Mika Pettersson contributed to the research. The research was published in the Nanoscale on xx.9.2016. Computational resources were supplied by CSC – IT Center for Science.
http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2016/nr/c6nr05267c#!divAbstract
- Full bibliographic informationTanja Lahtinen, Eero Hulkko, Karolina Sokołowska, Tiia-Riikka Tero, Ville Saarnio, Johan Lindgren, Mika Pettersson, Hannu Häkkinen and Lauri Lehtovaar,a, “Covalently linked multimers of gold nanoclusters Au102(p-MBA)44 and Au∼250(p-MBA)n” Nanoscale X x.x.2016, DOI: 10.1039/c6nr05267c
For further information, please contact:
Aila Pirinen+358295335092
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



