
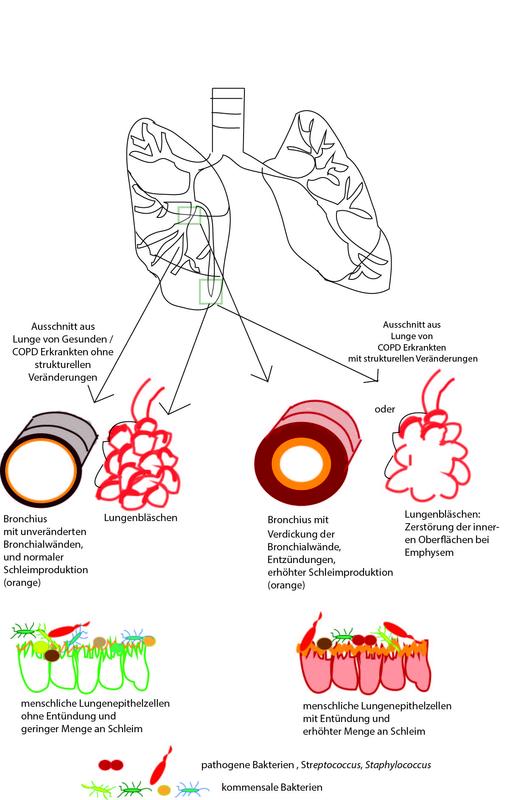
Infographics summarizing Engel et al.
Source: Helmholtz Zentrum München / Marion Engel
Coughing, breathing difficulties, and strong mucous production in the lungs are typical symptoms of COPD. The disease is often triggered by smoking, and, according to estimates from the World Health Organization (WHO), it could become the world’s third most common cause of death in 2030.
“COPD has various subtypes that, for example, can be verified by use of quantitative computer tomography (qCT)*,” explains PD Dr. Wolfgang zu Castell, head of the Research Unit Scientific Computing (ASC) at the Helmholtz Zentrum München. “We wanted to investigate if the microbiome in the lungs changes in a way that depends on these subtypes,” adds Prof. Dr. Michael Schloter, head of the Research Unit for Comparative Microbiome Analyses (COMI) at the Helmholtz Zentrum München.
Microbiome and CT scans analyzed
For this purpose, scientists from the two research units examined samples gathered from nine healthy individuals and 16 COPD patients. They were all participants of a Europe-wide population study (EvA Consortium; Emphysema versus Airways Disease). On the one hand, CT scans were used to analyze the lungs and assign the patients to the respective COPD subtypes. On the other hand, the scientists used brush samples from lungs to determine the composition of the lung microbiome using certain marker genes.
“This allowed us to show that the composition of the bacterial community in the lungs of COPD patients without structural changes is very similar to that of healthy subjects,” explains Dr. Marion Engel, scientist in the Complex Systems Research Group in the ASC and the study’s first author. “On the other hand, the bacterial composition in the lungs of ill subjects with structural changes differ significantly from those of the other two groups, regardless of the severity of the disease.”
Streptococci suspected
According to the study, Streptococci are often found in structurally altered lungs. This genus includes many pathogenic representatives that are also often detected in the presence of exacerbations**. In the lungs of healthy subjects, on the other hand, there was an increased presence of the genus Prevotella, to which a number of probiotic characteristics have also been attributed.
Taken together, these findings indicate that for certain subtypes of COPD, changes occur in the bacterial communities in the lungs that can promote an increase of potentially pathogenic bacteria. With regards to personalized medicine, it would therefore be expedient also to keep an eye on the microbiome, for instance when considering whether or not antibiotics or glucocorticoids should be administered in the event of a particular COPD subtype.
Further Information
* Unlike conventional computer tomography (CT), quantitative (q) methods analyze the physical density with great precision.
** Exacerbations denote a (mostly non-linear) progression of the symptoms
Background:
The presence of bacteria in the lungs is absolutely normal. It was also previously known that the composition of the bacterial communities in the lungs are changed in people with progressive COPD and that pathogenic bacteria and viruses can exacerbate the state of health, according to the authors. What is primarily new here is that structural changes in COPD patient lungs that can be detected with CT are associated with the composition of the lung microbiome, but not with the severity of the disease.
Original Publication:
Engel, M. et al. (2017): Influence of Lung CT Changes in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) on the Human Lung Microbiome. PLOS ONE, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180859
The Helmholtz Zentrum München, the German Research Center for Environmental Health, pursues the goal of developing personalized medical approaches for the prevention and therapy of major common diseases such as diabetes and lung diseases. To achieve this, it investigates the interaction of genetics, environmental factors and lifestyle. The Helmholtz Zentrum München is headquartered in Neuherberg in the north of Munich and has about 2,300 staff members. It is a member of the Helmholtz Association, a community of 18 scientific-technical and medical-biological research centers with a total of about 37,000 staff members. http://www.helmholtz-muenchen.de/en
The Scientific Computing Research Unit (ASC) is a part of the Institute of Computational Biology (ICB). The research unit combines the organization of the central data center of the Helmholtz Zentrum München with research components in scientific computing. Therefore the mission of the research unit is twofold: First, to provide professional ICT services for all organizational units of the Helmholtz Zentrum München. Second, to develop and apply mathematical methods for computational analysis and simulation of biological systems. http://www.helmholtz-muenchen.de/asc
The Research Unit for Comparative Microbiome Analyses (COMI) strives to elucidate elementary modes of action in microbiome development and the associated formation of networks which occur independently from any particular environment and can thus be considered as general principles of microbe – microbe interactions. A major issue will be to improve our understanding on the role of microbial networks for stability and resilience towards stressors or changing environmental conditions. This focus of research will not only unravel microbial functions in different environments, where microbes play an essential role, but it will also improve our in-depth understanding of microbiome interactions from different environments. Further results will allow the development of tools to restore microbiomes and thus improving the health of the hosts (contributing to the “red” and the “green” research fields of HMGU. http://www.helmholtz-muenchen.de/comi
Contact for the media:
Communication Department, Helmholtz Zentrum München – German Research Center for Environmental Health (GmbH), Ingolstädter Landstr. 1, 85764 Neuherberg – Tel. +49 89 3187 2238 – Fax: +49 89 3187 3324 – E-mail: presse@helmholtz-muenchen.de
Scientific Contact:
Dr. Marion Engel, Helmholtz Zentrum München – German Research Center for Environmental Health (GmbH), Research Unit Scientific Computing, Ingolstädter Landstr. 1, 85764 Neuherberg, Germany – Tel. +49 89 3187 1226 – E-mail: marion.engel@helmholtz-muenchen.de
http://www.helmholtz-muenchen.de/en/press-media/press-releases/all-press-releases/index.html – Read more news of Helmholtz Zentrum München












