CWRU researchers find a chemical solution to shrink digital data storage
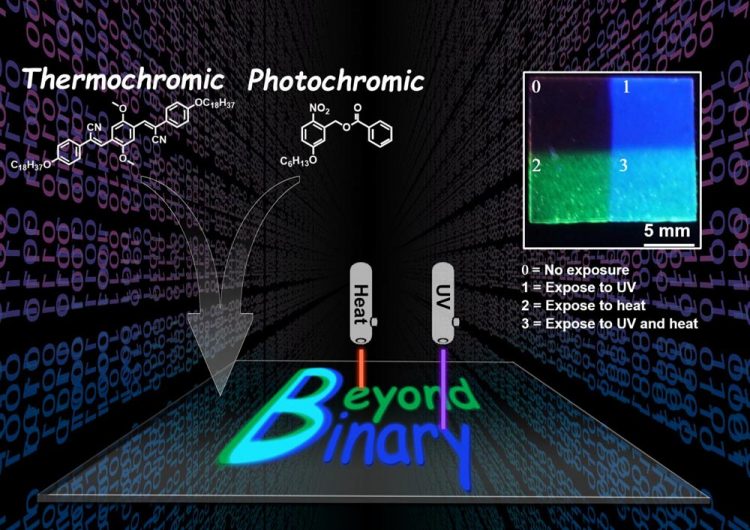
CWRU chemists developed a space-saving method to store digital data optically, using four-symbol, or quaternary code. The four symbols are the absence of color and three colors -- fluorescent green, ultramarine and cyan -- produced when dyes contained in a common polymer are exposed to heat, ultraviolet light or both. Credit: Emily Pentzer
From supercomputers to smartphones, the amount of data people generate and collect continues to grow exponentially, and the need to store all that information grows with it.
Computers and other digital devices operate and store data using a binary code, meaning two symbols–typically the numerals 0 and 1– represent information. To reduce storage space, engineers have traditionally used existing technology but made it smaller.
For example, a compact disc is made with a red laser and a Blu-ray disc with a blue, more focused, laser that reduces the size of the symbols and the space between them, increasing data density.
But according to a new study published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry C., researchers at Case Western Reserve demonstrate how commonly used polymer films containing two dyes can optically store data in a quaternary (four-symbol) code, potentially requiring about half as much space.
“We're using chemistry instead of engineering to address data storage, but it's really complementary to what engineers are doing,” said Emily Pentzer, assistant professor of chemistry at Case Western Reserve and study author. She worked with PhD students Peiran Wei and Bowen Li and Research Assistant Al de Leon on the project.
How it works
To take advantage of the quaternary storage, computer programs would need to be written in quaternary code instead of binary code, which Pentzer said would be easy with the system they used.
Instead of numerals, the optical-storage system uses the absence of color and three colors produced by the dyes as the symbols representing information.
The study
The researchers loaded a small amount–less than .4 percent by weight–of the two dye molecules into a flexible sheet of poly(methyl methacrylate), a polymer film called PMMA. PMMA is clear and colorless in ambient light and temperature.
One dye, cyano-substituted oligo(p-phenyene vinylene) fluoresces green when exposed to heat. The second dye, o-nitrobenzyl ester of benzoic acid, fluoresces ultramarine when exposed to ultraviolet light. When the overlapping dyes are exposed to both heat and UV light, they fluoresce as cyan.
Pentzer's team wrote code by laying metal or wood templates over the dye-containing film, then applying heat and ultraviolet light. They cut their templates and applied code using facilities at Case Western Reserve's Larry Sears and Sally Zlotnick Sears think[box].
Results and next steps
The circular symbols in the template were each 300 micrometers across, with 200 micrometers between them. The code proved durable, remaining legible even after the film had been rolled, bent, written on with permanent marker, submerged in boiling water and half the surface had been rubbed away with sandpaper.
The team is now investigating the use of specialized lasers to shrink the spatial resolution and therefore increase the data density (think CD vs. Blu-ray).
They are also investigating whether a third dye can be added that responds to different stimuli and remains distinct from the other two. If so, the colorless film, plus all the color combinations available, would allow the research team to store data using a septenary, or seven-symbol code, further shrinking storage.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



