
Europe's new X-ray laser reveals structure of antibiotic-disabling enzyme
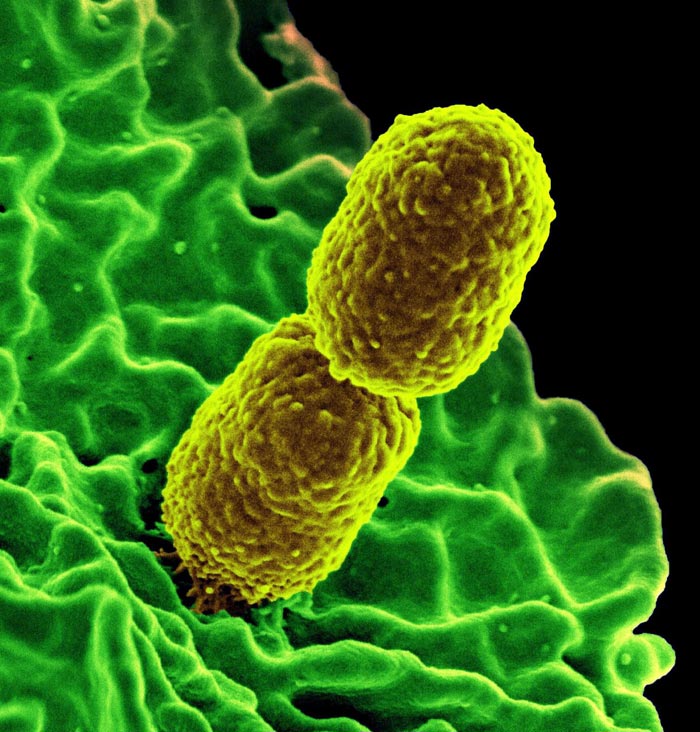
False-colored scanning electron microscope image of two Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteria (yellow) interacting with a human white blood cell (green).
Klebsiella pneumoniae, a bacterial enzyme that plays an important role in antibiotic resistance was examined by the new European XFEL instrument. (Klebsiella measures 1 to 2 microns long.)
Credit: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
An international collaboration led by the Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron or DESY, with participation from Arizona State University's Biodesign Center for Applied Structural Discovery, the Department of Physics and the School of Molecular Sciences, has announced the results of the first scientific experiments at Europe's new X-ray free-electron laser, European XFEL.
Over 120 international researchers collaborated on the study, whose findings–including the first new protein structure solved at the European XFEL–are reported in the advanced online edition of the journal Nature Communications.
Petra Fromme, director of the Biodesign Center for Applied Structural Discovery underlines the significance of the first research study carried out using the new European XFEL: “One of the most exciting capabilities of X-ray lasers is being able to make movies of life's most important processes at the atomic level. Our pioneering experiments at the European XFEL proved that you can resolve images that are only a millionth of a second apart.
The pioneering work not only demonstrates that the new research facility can speed up experiments by an order of magnitude, it also reveals a previously unknown structure of an enzyme responsible for antibiotic resistance.
“The groundbreaking work of the first team to use the European XFEL has paved the way for all users of the facility who greatly benefit from these pioneering experiments,” emphasizes European XFEL managing director Robert Feidenhans'l. “We are very pleased – these results show that the facility works even better than we had expected and is ready to deliver new scientific breakthroughs.”
“Being at a totally new class of facility, we had to master many challenges that nobody had tackled before,” says DESY scientist Anton Barty, from the Center for Free-Electron Laser Science (CFEL), who led the team of about 125 researchers, involved in the first experiments that were open to the whole scientific community. “I compare it to the maiden flight of a novel aircraft: All calculations and assembly completed, everything says it will work, but not until you try it do you know whether it actually flies.”
The European XFEL is designed to deliver X-ray flashes every 220 nanoseconds (0.000 000 220 seconds). To unravel the three-dimensional structure of a biomolecule, such as an enzyme, the pulses are used to obtain flash X-ray exposures of tiny crystals of that biomolecule. Each exposure gives rise to a characteristic diffraction pattern on the detector. If enough such patterns are recorded from all orientations of a crystal, the atomic structure of the biomolecule can be calculated. However, every crystal can only be X-rayed once since it is vaporized by the intense flash (after it produced a diffraction pattern). So, to build up the full three-dimensional structure of the biomolecule, a new crystal has to be delivered into the beam in time for the next flash, by spraying it across the path of the laser in a water jet.
Nobody has tried to image molecules with X-rays at atomic resolution at this lightning pace before. The fastest pulse rate so far of any such X-ray laser has been 120 flashes per second, that is one flash every 0.0083 seconds (or 8, 333, 333 nanoseconds). To probe biomolecules at full speed, the water jet carrying the tiny crystals (which are also vaporized by the X-rays), must recover in time to be able to replenish the crystals fast enough.
“We revved up the speed of the water jet carrying the samples to 220 miles per hour, that's about as fast as the speed record in Formula 1,” explains Max Wiedorn, who led the sample delivery together with his colleague Dominik Oberthür, both from CFEL. A specially designed nozzle, whose development was led by Saša Bajt, a Group Leader at DESY, was critical to ensuring the high-speed jet would be stable and meet the requirements.
To record X-ray diffraction patterns at this fast rate, an international consortium led by DESY scientist Heinz Graafsma designed and built one of the world's fastest X-ray cameras, tailor-made for the European XFEL. The 'Adaptive Gain Integrating Pixel Detector' (AGIPD) can not only record images as fast as the X-ray pulses arrive, it also automatically tunes the sensitivity of every pixel individually, providing much more accurate measurements of the diffraction patterns in which the information on the atomic structure of the sample is encoded. “The requirements of the European XFEL are so unique that the detector had to be designed completely from scratch and tailored to this task,” reports Graafsma, who heads the detector group at DESY's Photon Science division and is also a professor at the Mid Sweden University. “This could only be achieved thanks to the comprehensive expertise and fruitful collaboration of the large team involved.”
“It was exciting and somewhat nostalgic to see the first protein diffraction patterns at the European XFEL appearing live, reminiscent of the first atomic-resolution SFX patterns we saw live at LCLS over 7 years ago, which marked the beginning of the high-resolution SFX era. Many of the same collaborators were involved in both historic experiments,” notes co-author Nadia Zatsepin, Research Assistant Professor in the Department of Physics at ASU who leads SFX data analysis in the NSF BioXFEL Science and Technology Center. “The ability to collect data much faster means we can determine many more frames of molecular movies with dramatically reduced amount of the precious samples, which can be critical for structure determination for many important biological samples, especially for studying dynamics. However, carrying out these very first experiments as part of commissioning the XFEL source and novel detector involved overcoming some unique challenges. The excellent results in this publication, and indeed the facilitating of SFX experiments following these pioneering efforts, is testament to the effective leadership and organization and sincere camaraderie of this large collaboration.”
The scientists first determined the structure of a very well-known sample, the enzyme lysozyme from egg-white, as a touchstone to verify the system worked as expected. Indeed, the structure derived at the European XFEL perfectly matches the known lysozyme structure, showing details as fine as 0.18 nanometres (millionths of a millimeter). “This is an excellent proof of the X-ray laser's performance,” underscores XFEL pioneer Henry Chapman, a leading scientist at DESY, Division Director of CFEL, and a professor at the University of Hamburg. “We are very excited about the speed of the analysis: Experiments that used to take hours can now be done in a few minutes, as we have shown. And the set-up that we used can even be further optimized, speeding up data acquisition even more. The European XFEL offers bright prospects for the exploration of the nanocosm.” The striking performance of the X-ray laser is also a particular success for the DESY Accelerator Division that operates the European XFEL and led the construction of the world's longest and most advanced superconducting linear accelerator, which drives the European XFEL.
As their second target, the team chose a bacterial enzyme that plays an important role in antibiotic resistance. The molecule, designated CTX-M-14 β-lactamase, was isolated from the bacterium Klebsiella pneumoniae whose multidrug-resistant strains are a grave concern in hospitals worldwide. Two years ago, a 'pandrug-resistant' strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae–unaffected by all 26 commonly available antibiotics– was identified in the U.S., according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The bacterium's enzyme CTX-M-14 β-lactamase, is present in all strains. It works like a molecular pair of scissors, cutting open the lactam rings of penicillin-derived antibiotics open, thereby rendering them useless. To avoid this, antibiotics are often administered together with a compound called avibactam that blocks the molecular scissors of the enzyme. Unfortunately, mutations change the form of the scissors. “Some hospital strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae are already able to cleave even specifically developed third generation antibiotics,” explains Christian Betzel, co-author of the paper and also a professor at the University of Hamburg. “If we understand how this happens, it might help to design antibiotics that avoid this problem.”
The scientists investigated a complex of CTX-M-14 β-lactamase from the non-resistant, 'wild type' of the bacterium with avibactam bound to the enzyme's active center, a structure that has not been analyzed before. “The results show with 0.17 nanometer precision, how avibactam fits snug into a sort of canyon on the enzyme's surface that marks its active center,” says Markus Perbandt from the University of Hamburg, also a co-author of the paper. “This specific complex has never been seen before, although the structure of the two separate components were already known.”
These successful measurements show that it is possible to record high-quality structural information, which is the first step towards recording time-resolved snapshots of the biochemical reaction between enzymes and their substrates at different stages, using the European XFEL. Together with the research group of co-author Martin Aepfelbacher and Holger Rohde, professors at the University Hospital UKE in Hamburg, the team plans to use the X-ray laser as a film camera to assemble those snapshots into movies of the molecular dynamics of avibactam and this β-lactamase. “Such movies would give us crucial insights into the biochemical process that could one day help us to design better inhibitors, reducing antibiotic resistance,” says Betzel.
Movies of chemical and biochemical reactions are just one example of a whole new spectrum of scientific experiments possible at the European XFEL. The truly breakthrough feature is the rate at which data can be collected. “This opens up new avenues of structural discovery,” highlights European XFEL scientist Adrian Mancuso, who heads the SPB/SFX instrument (Single Particles, Clusters and Biomolecules & Serial Femtosecond Crystallography) where the pioneering experiments were done. “The difference in rate of discovery possible using European XFEL demonstrated by this experiment is as dramatic as the difference in travel time between being able to catch a plane across the Atlantic rather than taking a ship. The impact is potentially enormous.”
This first 'beamtime' for experiments at the European XFEL took place two weeks after the opening of the facility in September 2017, and was open to all scientists from the community to participate, contribute, learn, and gain experience in how to carry out such measurements at this facility. “The success of this 'open science' policy is illustrated by – among other things – the rapid dissemination of results from later campaigns at the SPB/SFX instrument by participating groups,” explains Chapman. “Additionally, the large concentration of effort by the community addressed previously unsolved challenges of managing and visualizing data – crucial to conducting all serial crystallography experiments at the European XFEL.”
“This work at the European XFEL is very important for the study of biological processes, as it will enable the study of biological reactions in real time. As the scientific director of the BioXFEL Science and Technology Center, which is supported by the National Science Foundation, I am very excited that members of the BioXFEL STC have made major contributions to this exciting first user experiment at the European XFEL” says Dr. John Spence, professor at the Department of Physics at Arizona State University.
###
Participating in the experiments from Arizona State University were Dr. Petra Fromme, director of the Biodesign Institute Center for Applied Structural Discovery (BCASD), Research Professor Nadia Zatsepin from the Department of Physics, NSF BioXFEL STC and BCASD, and Marc Messerschmidt from the European XFEL, NSF BioXFEL STC (now at BCASD).
About CFEL and DESY
The Center for Free-Electron Laser Science CFEL is a cooperation of the University of Hamburg, the Max Planck Society and DESY. DESY is one of the world's leading particle accelerator centers. Researchers use the large?scale facilities at DESY to explore the microcosm in all its variety – ranging from the interaction of tiny elementary particles to the behavior of innovative nanomaterials and the vital processes that take place between biomolecules to the great mysteries of the universe. The accelerators and detectors that DESY develops and builds at its locations in Hamburg and Zeuthen are unique research tools. DESY is a member of the Helmholtz Association and receives its funding from the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) (90 percent) and the German federal states of Hamburg and Brandenburg (10 percent).
About the Biodesign Center for Applied Structural Discovery
The Center for Applied Structural Discovery (CASD) unites a team of complementary research professionals from a wide range of disciplines, including biology, chemistry, physics and engineering, to develop and apply groundbreaking technologies and methodologies to accelerate the rate at which we discover the structure and associated function of biomolecules. Breakthrough knowledge will form the basis for fast progress on the path to technical innovations that improve human health and provide plentiful clean energy and food for future generations. The CASD mission is to develop new revolutionary techniques that reveal the structure and dynamics of biomolecules towards new visionary discoveries in medicine and energy conversion. biodesign.asu.edu/applied-structural-discovery
About NSF BioXFEL STC
Reference
“Megahertz serial crystallography”; Max O. Wiedorn, Dominik Oberthür, Richard Bean, Robin Schubert, Nadine Werner et al.; Nature Communications, 2018; DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-06156-7
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory's Linac Coherent Light Source I and II
https:/
Science contacts
– Dr. Anton Barty, CFEL/DESY, +49 40 8998-5783, anton.barty@desy.de
– Prof. Henry Chapman, CFEL/DESY, +49 40 8998-4155, henry.chapman@desy.de
– Prof. Christian Betzel, University of Hamburg, +49 40 8998-4744, christian.betzel@uni-hamburg.de
– Dr. Adrian Mancuso, European XFEL, +49 40 8998-2512, adrian.mancuso@xfel.eu
– Dr. Petra Fromme, Arizona State University, +1 480 326 7840
Press contact
Dr. Thomas Zoufal, DESY press officer, +49 40 8998-1666, presse@desy.de
Richard Harth, Biodesign Institute Senior Science Writer 480-727-0378 richard.harth@asu.edu















