
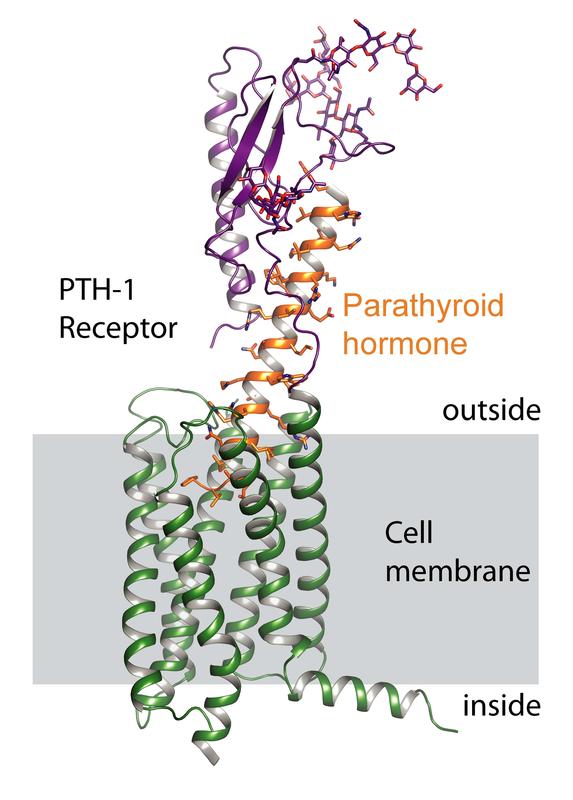
The PTH-1 receptor consists of an extracellular part (purple) and a part that resides in the membrane (green). Parathyroid hormone (orange) activates the receptor.
University of Zurich
Osteoporosis affects about 400,000 people in Switzerland, mostly women after menopause. It is often described as a silent disease, because bone loss usually occurs little by little over the years and without any symptoms.
The body gradually absorbs calcium from the bones, which become brittle. This process is controlled via what is called the parathyroid hormone (PTH) and a closely related peptide – a protein fragment.
They bind to the PTH-1 receptor, thereby telling the body to either release calcium from the bone or to build new bone.
An extremely difficult undertaking
A team led by Andreas Plückthun, professor at the Department of Biochemistry of the University of Zurich (UZH), has now been able to determine the three-dimensional structure of the PTH-1 receptor.
The atomic structure can now serve as the blueprint for the future development of drugs. Such receptor-binding compounds may slow down, and perhaps even reverse, osteoporosis to some degree.
Determining the structure of this receptor was an extremely tough undertaking, as cells only produce a very small amount of it, and it is also very unstable.
“The directed evolution and protein engineering methods we have developed over the last few years were absolutely instrumental in making this possible,” explains Andreas Plückthun.
Disadvantages of current treatment
One of the most effective current treatments for severe osteoporosis involves the use of substances that look like the natural hormone and its related peptide.
“However, this treatment is extremely expensive. The substances have to be injected into the thigh or abdomen once a day, and the treatment also has significant side effects,” says Christoph Klenk, co-author of the study.
The scientists are convinced that thanks to the new insights into the mechanisms of the PTH-1 receptor, new drugs can be developed that don’t have any of the previous disadvantages.
“The receptor is like a lock, and the peptides are the keys that turn it,” describes Plückthun. “Having the atomic 3D blueprint on a computer screen gives us an unprecedented level of insight into how the lock actually works.”
Understanding a whole class of receptors
The PTH-1 receptor is a member of the family of G protein-coupled receptors. In particular, these include receptors that bind to other hormones, such as the ones involved in controlling diabetes.
The work by the UZH scientists thus also sheds light on how the whole family of receptors works, as the PTH-1 receptor was examined at the highest level of detail for any of these receptors so far.
This has enabled the scientists to describe similarities as well as differences to other class B receptors. “Having the blueprint of the lock doesn’t give us a key yet, but now it’s possible to build one,” says Andreas Plückthun.
Prof. Andreas Plückthun, PhD
Department of Biochemistry
University of Zurich
Phone: +41 44 635 55 70
E-mail: plueckthun@bioc.uzh.ch
Janosch Ehrenmann, Jendrik Schöppe, Christoph Klenk, Mathieu Rappas, Lutz Kummer, Andrew S. Doré, Andreas Plückthun. High-resolution crystal structure of parathyroid hormone 1 receptor in complex with a peptide agonist. Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, November 19, 2018. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-018-0151-4
https://www.media.uzh.ch/en/Press-Releases/2018/Osteoporosis.html












