
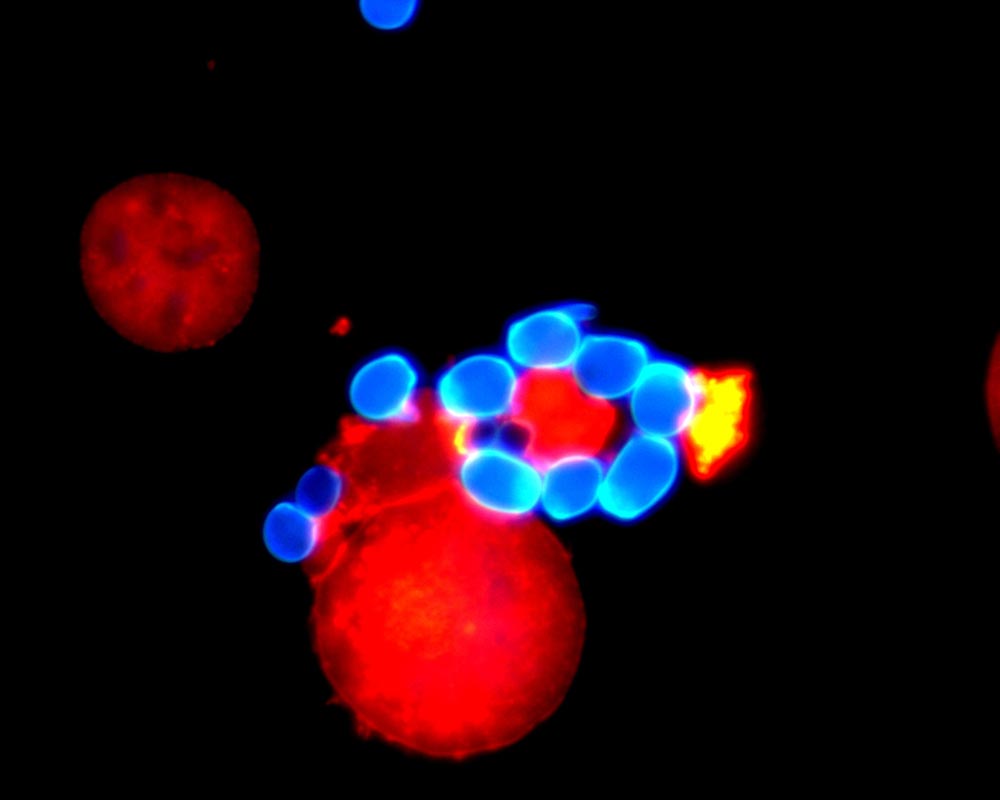
Macrophages (red) and the yeast Candida albicans (blue)
Source: Andrea Hartmann, Leibniz-HKI
Like many microorganisms, Candida albicans lives as a commensal, i.e. harmless beneficiary in the human digestive tract. It is part of a healthy microbiome. However, if the microbiome becomes unbalanced and the number of yeast cells increases, human macrophages intervene to regulate the fungus.
They absorb the fungus, which in return grows thread-like and produces the toxin Candidalysin. This toxin attacks the macrophages and destroys them. Thus Candida albicans escapes the grasp of the immune system and continues to multiply until the person eventually falls ill.
But it does not always come to that, as the research team from Germany, Great Britain, the USA and Canada has now discovered: the macrophage recognizes the toxin before it unfolds its deadly effect and triggers inflammation. This attracts other immune cells, especially neutrophils.
These finally eliminate the yeast. Candidalysin thus contributes on the one hand to the virulence of the pathogen by destroying host cells; on the other hand it fights itself by activating the immune defence. As a virulence factor, the toxin thus promotes the disease.
However, under certain circumstances it prevents it and is then an avirulence factor.
“It is possible that the dual function of Candidalysin we found is the result of the joint evolution of pathogen and host: The human immune system has learned to recognise the weapon of the pathogen and then launches the counterattack,” says group leader Bernhard Hube, head of department at the Leibniz-HKI and professor at the Friedrich Schiller University Jena. “We will now elucidate which conditions favour the avirulence property of Candidalysin over its toxicity,” Hube adds.
Bernhard Hube
bernhard.hube@leibniz-hki.de
Kasper L, König A, Koenig PA, Gresnigt MS, Westman J, Drummond, RA, Lionakis MS, Groß O, Ruland J, Naglik, JR, Hube B (2018) The fungal peptide toxin Candidalysin activates the NLRP3 inflammasome and causes cytolysis in mononuclear phagocytes. Nature Communications, DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-06607-1.












