
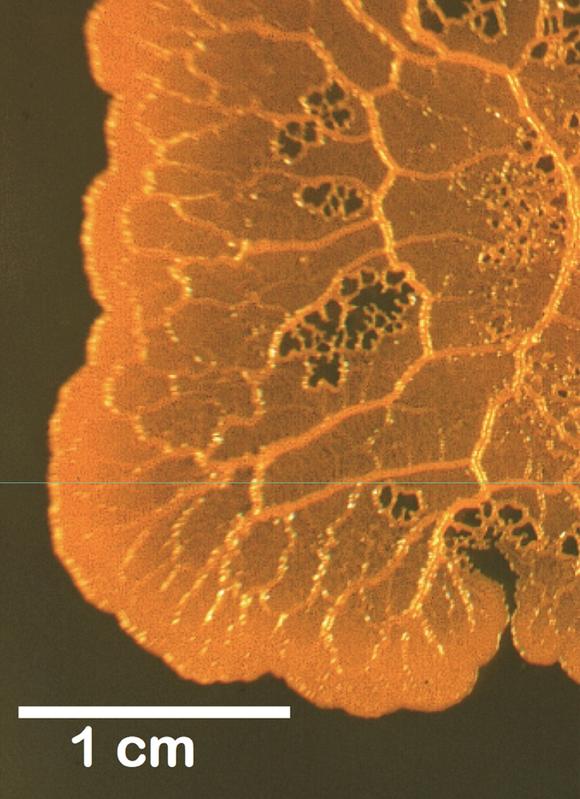
Giant cell of Physarum polycephalum.
Prof. Wolfgang Marwan
The “slime mold” Physarum polycephalum is an amazing creature. As a giant single cell it is visible with the naked eye. The yellow, slimy mass of protoplasm, which crawls over rotting logs engulfing its prey, seems as unusual as an alien from outer space.
One specimen, which entered the Guinness Book of Records in 1989, covered a surface area of 5.5 square meters and weighed approximately 3 kgs–obviously deserving its title as the largest single cell ever grown.
This enigmatic organism has also attracted the interest of physicists, engineers, and artists who have taken inspiration from Physarum for developing computer algorithms, or directly used giant Physarum cells for steering robots, creating art projects, or electronic music.
However, for biologists Physarum has been a sleeping beauty during the past decades, because almost nothing was known about its genome and genes. This shortcoming has now changed fundamentally.
In an upcoming issue of Genome Biology and Evolution, an international group of scientists reports on the sequence of the 188 million nucleotides that make up the Physarum genome. These nucleotides encode 34,000 genes, over 50% more than the human genome.
Few other organisms have thus far posed such difficulties in deciphering their genome, which called for improvements of existing sequencing technologies, according to Pat Minx from the McDonnell Genome Institute at Washington University.
Comparison of its genes with those of other species proved what biologists already suspected. The so-called slime mold is in reality not a mold (fungus) but a giant amoeba, belonging to the amoebozoa group of organisms.
In light of our contemporary understanding of molecular evolution, Physarum appears to be an ancient relic with similarity to the last common ancestor of Amoebozoa, fungi and animals (including humans): a prototypical cell from the era of early eukaryote evolution with some molecular features that were thought to be specific for either animals or plants.
For a single-celled organism, Physarum has a very extensive system for signal detection and processing. This network of interacting genes and proteins picks up signals from the cell’s external environment and internal state, processes the information in sophisticated ways, and makes decisions that control the behavior and development of the organism. The molecular complexity of this signalling system is comparable to, and in some respects exceeds, that of higher animals, making Physarum a good model organism for the analysis of how living cells interact with their environment.
For example, Physarum has an unparalleled diversity in proteins to synthesize and detect the intracellular messenger molecules, cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP. Additionally, like animal cells but unlike plants or fungi, Physarum uses tyrosine-kinase signaling proteins for information processing.
Because a related amoebozoon, Acanthamoeba, also employs tyrosine kinase signaling, one may conclude that tyrosine kinases were present in the last common ancestor of Amoebozoa, fungi, and animals rather than having appeared only later, in the animal lineage, as was commonly believed until recently, says Pauline Schaap from Dundee University.
Tyrosine kinases are enzymes that play important roles in controlling normal cell fates, and their misbehaviors have been implicated in diseases such as cancer, arteriosclerosis and diabetes. Comparing human cells with their evolutionarily very distant cousin, Physarum, may ultimately help to understand core mechanisms of health and disease by abstracting what really matters for cellular regulation, says Gernot Glöckner from the University of Cologne, a main investigator in this project.
An increasing number of biologists believe that analyzing changes in hundreds or even thousands of components in individual cells over time will be necessary to obtain essential information on how cellular functions are controlled. In this light, the genome sequence of Physarum, a classical organism for single cell research, has come just in time.















