HIV virulence depends on where virus inserts itself in host DNA
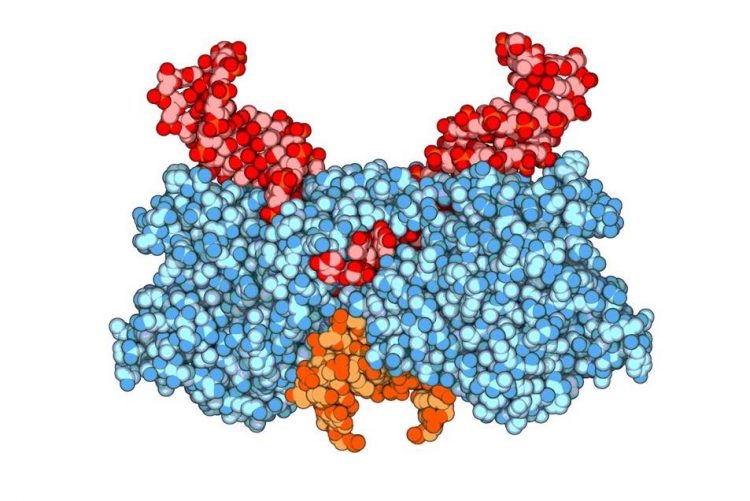
The HIV protein integrase (blue) can insert viral DNA (red) at different locations in the DNA of its human host (orange). But how the virus selects its insertion points has puzzled virologists for over 20 years.
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) can insert itself at different locations in the DNA of its human host – and this specific integration site determines how quickly the disease progresses, report researchers at KU Leuven’s Laboratory for Molecular Virology and Gene Therapy. Their study was published online today in the journal Cell Host & Microbe.
When HIV enters the bloodstream, virus particles bind to and invade human immune cells. HIV then reprogrammes the hijacked cell to make new HIV particles.
The HIV protein integrase plays a key role in this process: it recognises a short segment in the DNA of its host and catalyzes the process by which viral DNA is inserted in host DNA.
Integrase can insert viral DNA at various places in human DNA. But how the virus selects its insertion points has puzzled virologists for over 20 years.
Now a team of KU Leuven researchers has discovered that the answer lies in two amino acids. Doctoral researcher Jonas Demeulemeester, first author of the study, explains: “HIV integrase is made up of a chain of more than 200 amino acids folded into a structure. By modelling this structure, we found two positions in the protein that make direct contact with the DNA of the host. These two amino acids determine the integration site. This is not only the case for HIV but also for related animal-borne viruses.”
Viral variants
In a second phase of the study, the researchers were able to manipulate the integration site choice of HIV, explains Professor Rik Gijsbers. “We changed the specific HIV integrase amino acids for those of animal-borne viruses and found that the viral DNA integrated in the host DNA at locations where the animal-borne virus normally would have done so.”
“We also showed that HIV integrases can vary,” says Professor Rik Gijsbers. “Sometimes different amino acids appeared in the two positions we identified. These variant viruses also integrate into the host DNA at a different site than the normal virus does.”
Together with Dr. Thumbi Ndung’u (University of KwaZulu-Natal, Durban, South Africa), the team studied the impact of these viral variants on the progression towards AIDS in a cohort of African HIV patients, continues Professor Zeger Debyser: “To our surprise, we found that the disease progressed more quickly when the integration site was changed. In other words, the variant viruses broke down the immune system more rapidly. This insight both increases our knowledge of the disease and opens new perspectives. By retargeting the integration site to a ‘safer’ part of the host DNA, we hope to eventually develop new therapies.”
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

New organoid with all key pancreas cells
Researchers from the Organoid group (previously Clevers group) at the Hubrecht Institute have developed a new organoid that mimics the human fetal pancreas, offering a clearer view of its early development….

Tasty, Airy Baked Goods with Culinary Foam made from Peas
Culinary foam made from the whites of chicken eggs makes baked goods light and airy. In the LeguFoam project, Fraunhofer researchers are working on a plant-based alternative made from legumes….

Biohydrogen from Wood Waste
Up to now, wood waste has had to be disposed of at great expense and, at best, has been used to generate energy in incineration plants. Fraunhofer researchers are now…



