
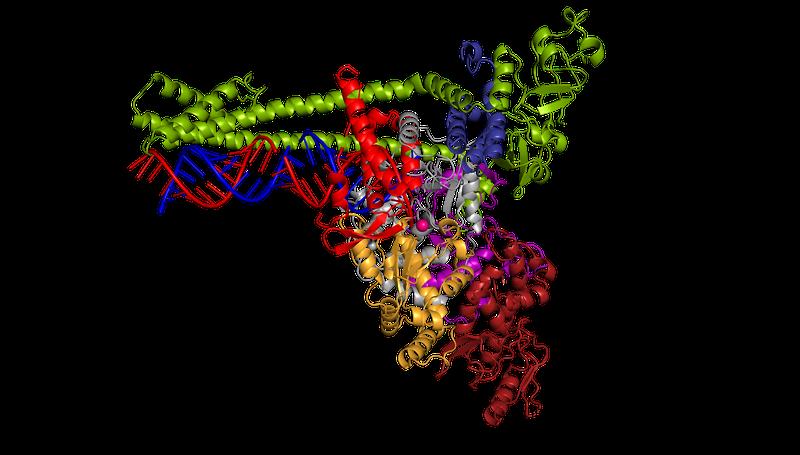
The polymerase of the new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 multiplies the pathogen's genetic material (blue and red).
© Lucas Farnung, Christian Dienemann, Hauke Hillen / Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry
“In view of the current pandemic we wanted to help,” Max Planck Director Cramer says. “We have extensive experience in studying polymerases.” It was therefore obvious to the scientists what project to choose.
“We were surprised to find that the structure of the coronavirus polymerase is special – it differs from other structures that we have been investigating so far,” explains Hauke Hillen. The coronavirus polymerase binds to the RNA in the same way as is known from other types of viruses.
However, this polymerase comprises an additional element with which it binds the RNA until it has copied the genetic material. This is important for the corona virus as its genome consists of around 30,000 building blocks and is therefore particularly long, making copying a major challenge.
Understanding in detail how antivirals work
Knowing how the coronavirus polymerase is constructed on an atomic scale opens up new possibilities to better understand and combat the pathogen. In the next step, Cramer's team will investigate in detail how antiviral substances block the proliferation of coronaviruses.
“Many hopes rest on remdesivir, which directly blocks the polymerase. With the structure at hand it might be possible to optimize existing substances such as remdesivir and to improve their effect. But we also want to search for new substances that are able to stop the virus polymerase,” Cramer says.
The Göttingen researchers have already published their results in a manuscript on the internet. “We wanted to immediately share our findings with the international scientific community to speed things up, now that we are in the middle of the pandemic,” reports Lucas Farnung, who will soon take up a professorship at Harvard University in the United States.
Corona polymerase at 100,000-fold magnification
The path to the three-dimensional structure of the corona polymerase was rocky. “First, we had to reconstitute the polymerase from three purified proteins. After some optimization, it was finally functional in the test tube,” explains Goran Kokic.
“Only then we were able to study how it works.” To do so, the scientist had quickly established a special test to determine the activity of the polymerase.
The team then examined the samples in the electron microscope with a magnification of more than 100,000-fold – and at first disappointment set in: “Although we took pictures around the clock for ten days and nights, we were unable to gain detailed insights into the structure,” recalls Christian Dienemann, an expert in electron microscopy.
“However, one sample looked different, somehow strange. Our first thought was to discard it. Fortunately, we did not: This sample, over all, provided us with the high-quality data we needed,” says Dimitry Tegunov, the group's data processing expert who also programmed the software to process large volumes of image data in a short time.
The determination of the polymerase structure will not be the last contribution of the Göttingen researchers to tackling the pandemic: “We are planning to take a look at the helper factors that change the viral RNA in such a way that it cannot be degraded by the human immune system,” Cramer says. “And of course, as structural biologists, we hope to find further targets in the virus that might open up new therapeutic strategies in the medium term.”
Prof. Dr. Patrick Cramer, Department of Molecular Biology
Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry
Phone: +49 551 201-2800
E-Mail: patrick.cramer@mpibpc.mpg.de
Hillen HS*, Kokic G*, Farnung L*, Dienemann C*, Tegunov D*, Cramer P*
(*equal contribution): Structure of replicating SARS-CoV-2 polymerase. Link to online pre-publication: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.27.063180v1
https://www.mpibpc.mpg.de/17275755/pr_2008 – Original press release of the Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry
https://www.mpibpc.mpg.de/cramer – Website of the Department of Molecular Biology of Patrick Cramer, Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry












