
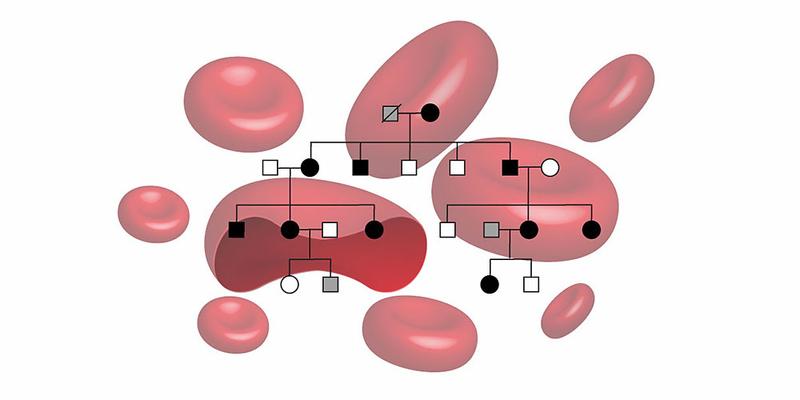
Inheritance of the familial erythrocytosis.
(Image: University of Basel, Department of Biomedicine)
In patients suffering from erythrocytosis, the red blood cell mass (erythrocytes) is exceptionally high. The disease is usually triggered by a genetic disorder in the bone marrow, which leads to increased production of red blood cells.
Researchers from the University of Basel and University Hospital Basel have now identified the first mutation in the EPO gene in a family with hereditary erythrocytosis. Ten affected family members from four generations took part in the study.
Using a genome-wide linkage analysis and gene sequencing, the researchers discovered that all of the affected family members lacked a single base in the EPO gene. As the EPO hormone increases the production of red blood cells, it was likely that this mutation caused the disease.
Overproduction instead of failure
However, the researchers were initially puzzled. This mutation would actually lead to a loss of function of the EPO gene, because the absence of the base shifts the reading frame of the genetic code, meaning that no more EPO protein can be formed. Despite this, the concentration of EPO hormone in the patients’ blood measurably increased rather than decreased.
The explanation was found using the CRISPR method, which allowed the researchers to engineer cells carrying the EPO mutation. There is a second, hidden mRNA in the EPO gene that is not normally involved in the production of a protein. As the researchers show, the mutation also leads to a shift in the reading frame of this second mRNA, this time with the result that more biologically active EPO hormone is produced.
“The mechanism is intriguing,” says study leader Professor Radek Skoda from the University of Basel’s Department of Biomedicine. “The mutation reprograms the gene product so that it gains a new function and is misused to overproduce EPO.” With consequences for the patients, who suffer from headaches and dizziness thanks to the increased red blood mass.
Mutations in the EPO gene should be taken into account in future searches for the causes of hereditary erythrocytosis, write the researchers in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Original source
Jakub Zmajkovic, Pontus Lundberg, Ronny Nienhold, Maria L. Torgersen, Anders Sundan, Anders Waage, and Radek C. Skoda
A Gain-of-Function Mutation in EPO in Familial Erythrocytosis
The New England Journal of Medicine (2018), doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1709064
Further information
Prof. Dr. Radek Skoda, University of Basel, Department of Biomedicine / University Hospital Basel, tel. +41 61 265 23 24, e-mail: radek.skoda@unibas.ch
https://www.unibas.ch/en/News-Events/News/Uni-Research/Inherited-mutation-leads-…












