
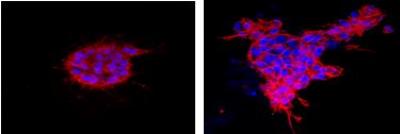
A human breast cell lacking HOXA5 (right) shows protruding structures similar to tumor cells, compared with a normal human breast cell (left).
Courtesy of Sara Sukumar, Ph.D.
In their study published online May 9 in the journal Oncogene, scientist Saraswati Sukumar, Ph.D.; her graduate student Wei Wen Teo; and their colleagues show that cells without HOXA5 have an increased capacity to renew themselves and are more invasive than normal breast cells — in short, they become more tumor like.
“Learning more about the biological impact of the HOXA5 protein, which is absent so frequently in breast cancers, may eventually help scientists develop new therapies to treat this disease,” says Sukumar.
The loss of HOXA5 leads to an increase in breast cells' “stemness and cell plasticity,” meaning they can more easily revert back to an undifferentiated state where they are capable of producing more new cells, says Sukumar, a professor of oncology and pathology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. Proteins that “promote features of plasticity will allow a tumor to thrive better,” she adds.
For the study, the researchers analyzed gene expression from human breast cell lines lacking HOXA5. They found that the protein seems to help maintain several traits in normal breast cells, including the ability to adhere to other epithelial cells, and the presence of molecules marking the cells as differentiated and not capable of self-renewal like breast stem cells.
When Sukumar and the others depleted the HOXA5 protein in other breast cell lines in the lab, the cells became more immature, or “stem like,” as well as more mobile. A closer look, she says, revealed that HOXA5 regulates the production of two other proteins: CD24 and E-cadherin. Without CD24, the cells begin to revert toward a stem like state, and without E-cadherin, cells lose some of the “glue” that binds them to other cells, says Sukumar.
As a result, breast cells without HOXA5 were more likely to grow aggressively in lab experiments, forming protruding structures similar to those seen as tumor cells begin to metastasize, the scientists found.
They then tested the behavior of human tumor cells with and without HOXA5 by injecting those cells into the mammary fat pad of mice. Results showed that tumor cells containing the protein carried anywhere from 10 to 17 times fewer breast stem cells, and tumors grown from the injected cells were about three times smaller than those in mice who had received tumor cells with depleted levels of HOXA5.
Sukumar and her colleagues also analyzed data from two international breast cancer genetic data sets and found that the lower the amount of HOXA5 in a tumor, the higher the grade of breast cancer in the patient. Similarly, patients with tumors containing low amounts of HOXA5 protein also had lower cancer relapse-free survival rates.
The scientists are planning further study of HOXA5's role in breast cancer, following up on this work and a study published by Sukumar's lab in 2000 that showed a connection between low levels of HOXA5 and the well-known tumor suppressor protein p53. Sukumar, who is the Barbara B. Rubenstein Professor in Oncology at the Kimmel Cancer Center, recently won a $300,000 grant from the Avon Foundation to continue the work.
###
Other Johns Hopkins scientists who contributed to the study include Vanessa F. Merino, Soonweng Cho, Preethi Korangath, Xiaohui Liang, Ren-chin Wu, Neil M. Neumann, and Andrew J. Ewald.
Funding for the study was provided by the Susan G. Komen Foundation Leadership Grant (SAC110050), the Department of Defense Center of Excellence (W81XWH-04-1-0595), the SKCCC Core grant (P30 CA006973) and the Avon Foundation Center of Excellence.












