
Healthy platelets have an organized actin cytoskeleton (red), surrounded by microtubules (green). In Patients with TRPM7 channel defect, it's damaged, but can be restored with magnesium.
Research Group Nieswandt
A low platelet count (thrombocytopenia) prevents wound healing. People with a coagulation disorder can lose too much blood during otherwise harmless gum bleeding or other injuries.
Platelets (thrombocytes) are created in the bone marrow continuously from megakaryocytes. The molecular biological regulation of this cytoskeletal-controlled process has not been completely analyzed yet.
In this publication, researchers provided for the first time several independent lines of evidence that TRPM7 (Transient receptor potential melastatin-like 7) regulates the balance of magnesium in megakaryocytes. Magnesium itself is involved in many metabolic processes and therefore essential for the body.
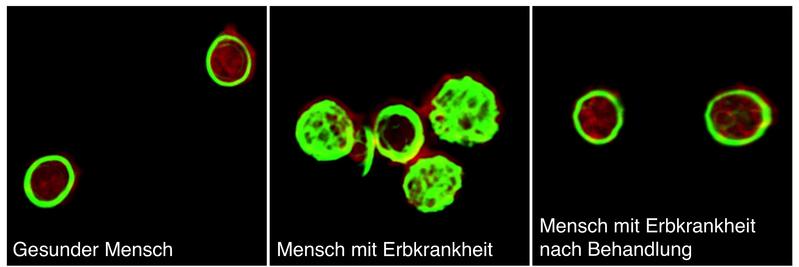
Researchers manipulated the channel function of TRPM7 in megakaryocytes of mice and observed severe damages in the structure of platelets, the so-called cytoskeleton. Consequently platelets were inoperative. Patient samples where a TRPM7 channel dysfunction has been then identified, had a low concentration of magnesium (Mg2+) in their platelets.
The platelets showed an unusual size and shape, an abnormal structure and excessive vacuoles. Interestingly, the supplementation of magnesium to the platelets of mice or patients restored this defect completely in the test tube.
The study indicates that special attention should be paid on the number and size of platelets during the diagnosis of an imbalanced magnesium condition, as a platelet deficiency may be present. “If there is a genetic defect of TRPM7, administration of magnesium could be used as a relatively safe therapeutic intervention,” hopes the leader of the study, Dr. Attila Braun.
The treatment would be cost effective and would have relatively few side effects. Further studies in animal models and patients (with altered TRPM7 channel function) have been initiated, in order to evaluate the efficacy and safety of magnesium as a therapeutic for this disease.
Researchers were particularly pleased about the direct correlation of mouse and patient data. “This was a huge advancement for the project”, says Prof. Bernhard Nieswandt, who managed the project together with Dr. Attila Braun.
Platelets are small cellular components in the blood. They play an important role in coagulation. In case of an injury, they seal the vascular wall temporarily. If this function is impaired due to damaged platelets, immoderate bleeding may occur.
http://www.rudolf-virchow-zentrum.de/en/news/news/article/neue-kostenguenstige-t…












