
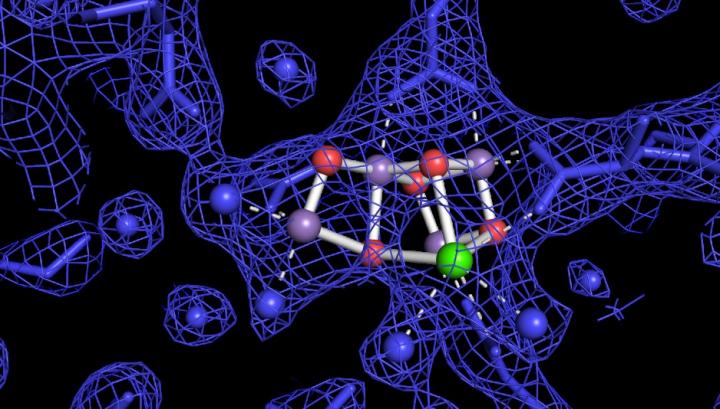
The structure of the complex in photosystem II where oxygen is evolving in a light-activated state. Water molecules are shown as blue spheres, the four manganese ions in purple, the calcium ion in green and the bridging oxygen ions in red. The blue mesh is the experimental electron density, and the blue sticks are the protein side chains holding the catalytic complex.
Credit: Johannes Messinger, Umeå University
“This work is a breakthrough. It paves way to study step-by-step the formation of an oxygen molecule by two water molecules,” says Johannes Messinger, professor in Biological Chemistry at Umeå University in Sweden and one of the leading researchers in the project.
Plants play a crucial role in mitigating climate change. They use sunlight to remove greenhouse gas carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and convert it into biomass. At the same time, plants also produce the oxygen we breathe by splitting water into oxygen and biologically bonded hydrogen. This process may prove even more important to save the climate, because if we understand water splitting completely, we can develop technology that produces hydrogen gas (fuel) from solar energy, which is much more efficient than how plants can produce biomass.
In collaboration with an international team of researchers, professor Johannes Messinger, who recently joined the Molecular Biomimetics Programme at Uppsala University, has now found a way to visualise this reaction in high-resolution images using the X-ray free-electron laser at SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory at Stanford University.
In the study, published in the current issue of the journal Nature, the research consortium developed new ways to grow microcrystals of photosystem II – the protein complex in plants that is responsible for producing oxygen from water using sunlight. These microcrystals were then placed on a conveyor belt using technology akin to ink-jet printing. On the belt, the crystals were illuminated with laser flashes of green light, to start the water splitting reaction cycle. During this process, the protein complex undergoes a series of steps before the oxygen process starts.
The structure of these activated states were subsequently visualised by hitting the crystals with ultrafast X-ray pulses (10-15s). The present scientific article describes how the authors were able to resolve the structural differences between two of the states in photosystem II that are involved in water splitting.
“We are now all set to tackle the final mysteries of how plants make oxygen – a dream has come true,” says Johannes Messinger.
In order to make the promising progress, research teams from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Stanford University in the US, Humboldt University in Berlin, Umeå University and Uppsala University in Sweden have collaborated for five years.
Media Contact
Ingrid Söderbergh
ingrid.soderbergh@umu.se
46-706-040-334
http://www.












