
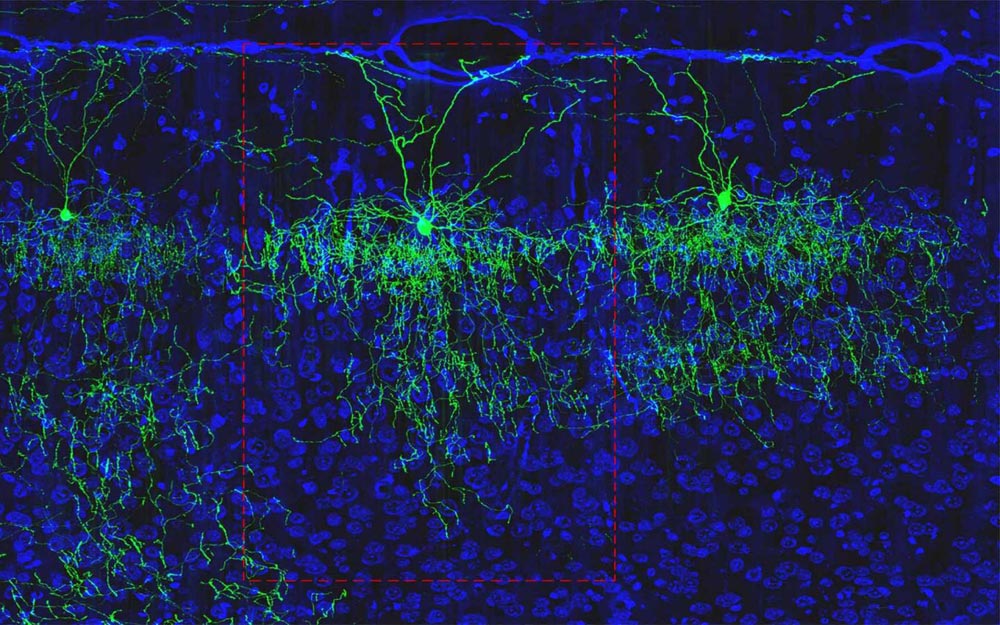
Pictured is an axo-axonic cell (AAC) found in the cortex of a mouse brain. Huang and his colleagues discovered that there are multiple subtypes of AACs. Each is distinguished by the arrangement of important connections the chandelier-shaped cells form with neighboring neurons.
Credit: Wang et al. Cell Reports 2019
So, why is this necessary? Think of it this way: if you were mapping a city, you'd want a sensible system for identifying streets, buildings, and landmarks, and understanding the distinctions between them. In a similar way, in mapping a brain, it's logical to name and distinguish between neuronal types in order to understand how they relate to each other.
CSHL Professor Z. Josh Huang, a project leader at the Center for the Mouse Brain Cell Atlas, explains that to classify a neuron as a specific neuronal type, “what is needed is a comprehensive image of a whole cell, and then to label the cells that are like it–to quantify those and to register them in the whole brain to compare. This has never been achieved, but technology is finally catching up.”
Now, in the latest issue of Cell Reports, Huang and colleagues from the US and China describe how they've created a process for classifying neurons in a mouse brain in a suitably comprehensive manner.
According to the team, the new platform embraces four major aspects of brain mapping:
First, the team identifies and labels neurons of the same shape by discerning key genetic clues that are unique to the cell type. Importantly, because this genetic information describes how a neuron's synapses are structured, it can also indicate with which other cells a neuron is capable of communicating.
Second, through cutting-edge technology, the scientists are able to image the entire brain. This “wide angle” look at a neuronal type's home regions provides exceptionally important context for the third aspect: reconstruction.
By pairing imagery and genetic labeling at the single-neuron resolution with an “atlas” of the whole brain, the team can painstakingly “reconstruct” a brain, providing data on each and every neuronal type's location.
Lastly, with this information about shape, connectivity, and location in hand, computational biologists can crunch the numbers, determining what is relevant and unique to any one cell type, and what is not.
As a proof-of-concept, Huang and CSHL computational neuroscientist Partha Mitra looked specifically at axo-axonic cells (AACs) found in the cortex. Despite already being remarkably specific in location, shape, and purpose, the team determined that there are actually a wide variety of AAC subtypes.
According to Huang, the BRAIN Initiative will continue to refine their process until neuron classification is not only easy, but second nature in the quest to accurately map an entire brain.
###
About Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory
Founded in 1890, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory has shaped contemporary biomedical research and education with programs in cancer, neuroscience, plant biology and quantitative biology. Home to eight Nobel Prize winners, the private, not-for-profit Laboratory employs 1,100 people including 600 scientists, students and technicians. The Meetings & Courses Program annually hosts more than 12,000 scientists. The Laboratory's education arm also includes an academic publishing house, a graduate school and the DNA Learning Center with programs for middle and high school students and teachers.
For more information, visit http://www.












