
The “classical” bacteria responsible for methane uptake are small and round. Mass spectrometry reveals that methane is also assimilated by much larger, filamentous Crenothrix.
Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology
When decaying organic matter sinks to the bottom of a lake or ocean, methane is produced as the biomass is broken down. Some of the methane is released from the surface into the atmosphere, where it acts as a potent greenhouse gas, while some is broken down by microorganisms in the water column.
An international research group around Kirsten Oswald from Eawag (Switzerland) and Jana Milucka from the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology in Bremen now reports that, as well as the “classical” methane consumers, filamentous bacteria of the genus Crenothrix are also involved in the methane removal process. The study has just been published in The ISME Journal.
Chance discovery
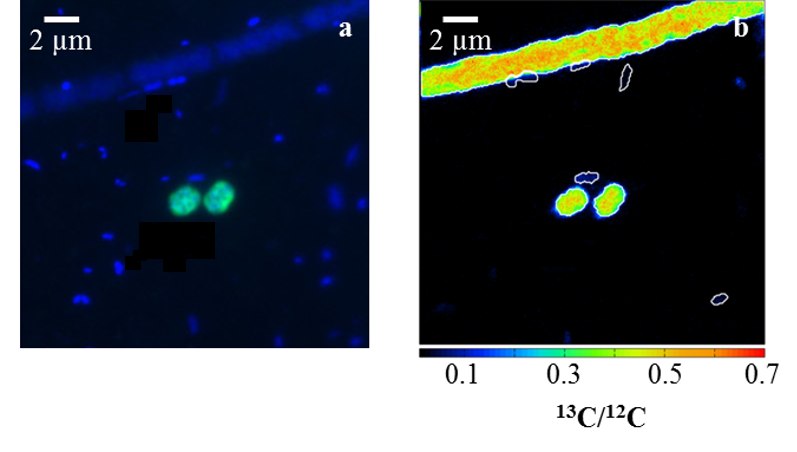
The role played by Crenothrix bacteria – previously little studied in the environment – was discovered by chance, when the researchers were seeking to quantify methane removal in the Rotsee (Canton Lucerne) and Lake Zug with the aid of stable isotope labelling. In this method, methane molecules are labelled with heavy carbon-13 atoms; when 13C-labelled methane is assimilated by bacteria, the individual cells can be visualized by means of imaging mass spectrometry.
“Typically these are small round or rod-shaped cells”, says Jana Milucka. In this case, however, the bacteria enriched with 13C were not only single round cells but also long, filamentous varieties (see photo). This finding was very surprising, as so far the researchers didn’t know these filamentous bacteria could occur so abundantly in nature. “We then started wondering about their role in the environmental removal of methane”, says Milucka.
Commonly known as well-thread
Eawag geologist Carsten Schubert – an expert on microbial degradation of methane in water – was also surprised by the group’s findings in the two Central Swiss lakes. While the large filamentous Crenothrix bacteria have long been known, they are only familiar as a contaminant in drinking water systems (hence their name “well-thread”), where their proliferation can cause clogging of pipes, sand filters and screens.
Crenothrix bacteria have not previously been detected in lake water, because they have not been specifically sought and they are difficult to identify with molecular genetic methods. Schubert concludes: “We seem to have completely underestimated their role in the biogeochemical cycle.” The researchers have now shown that Crenothrix are not only a stable part of the microbial community in freshwater lakes but may even be the most important methane consumers.
Original publication
Kirsten Oswald, Jon S Graf, Sten Littmann, Daniela Tienken, Andreas Brand, Bernhard Wehrli, Mads Albertsen, Holger Daims, Michael Wagner, Marcel MM Kuypers, Carsten J Schubert and Jana Milucka (2017): Crenothrix are major methane consumers in stratified lakes; ISME Journal (2017) 00, 1–17. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2017.77
Please direct your queries to
Dr. Jana Milucka
Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology
Phone: +49 421 2028 634
E-Mail: jmilucka@mpi-bremen.de
or the press office
E-Mail: presse(at)mpi-bremen.de
Dr. Fanni Aspetsberger
Phone: +49 421 2028 947
Dr. Manfred Schlösser
Phone: +49 421 2028 704
Text: Andri Bryner (Eawag)












