
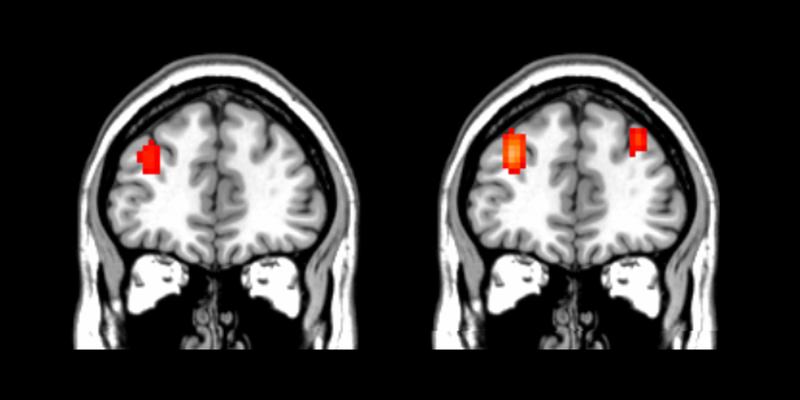
Brain activity of a younger test subject doing spatial memory tasks – left side: solving a simple task, right side: solving a very difficult task.
Copyright: Axel Lindner
As we get older, our brain mobilises additional capacity whenever it is particularly challenged. According to the current paradigm, the aging brain makes use of areas in both hemispheres, while only using one hemisphere for each task at a younger age.
A team of researchers at the department of cognitive neurology at the Hertie Institute for Clinical Brain Research (HIH) led by Dr Axel Lindner has now investigated specifically when this mechanism is engaged. Employing functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), they observed the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC), a brain area responsible for memory tasks. They found that the dlPFC is active in both hemispheres whenever faced with especially difficult tasks – not only in elderly but also in younger people.
For every cognitive task, characteristic brain areas specalised in that task are active. In most cases, these specialised areas are much more active in one hemisphere; language processing, for instance, happens mostly in the left hemisphere. Neuroscience calls this hemispheric division of tasks ‘lateralisation of brain functions’.
According to recent studies, this lateralisation is partly offset in elderly people: memory tasks leading to one-sided activity in young test subjects show both hemispheres as active in older subjects. The current hypothesis is that the brain mitigates its own age-related erosion by drawing on performance reserves in the other hemisphere.
The HIH researchers – with support from the Werner Reichardt Centre for Integrative Neuroscience (CIN) at the University of Tübingen and the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE) – set out to investigate when exactly this happens. Earlier studies had posed the same tasks to all probands. Maybe younger probands were simply less challenged by the same tasks? Working memory performance varies between individuals and decreases with age.
The Tübingen scientists therefore ensured that all probands received tasks which were subjectively equally difficult, some of them approaching the limits of the probands: repeated memorisation of changing rows of letters, of spatial positions or of complex figures. Using fMRI, the scientists monitored and compared memory activity in both hemispheres of the dlPFC.
The result was surprising: the test subjects were able to solve easy tasks according to expectations, with only the left hemisphere of the dlPFC showing increased activity. For difficult tasks, both hemispheres showed increased activity – however, this occurred not only in elderly subjects, but also in younger. Therefore, temporary enhancement of ‘computing power’ through bilateral operation of otherwise unilaterally active brain areas is not a compensation mechanism of the aging brain.
Offset of lateralisation may have been first observed in elderly people, but this is only because our working memory tends toward weaker performance at old age. It is still an open question why that is the case. Perhaps our memory does not really get weaker as we grow older, but the numbers of individual memories pile up so much that overall performance is impaired, as postulated by the Tübingen linguist Michael Ramscar.
‘Our data rather fits with that hypothesis’, says Melanie Höller-Wallscheid, who conducted the study as part of her doctoral studies. ‘We were never very clear on how the brain is supposed to develop an all-new mechanism as it ages, even though this is practically the current paradigm. Now our study demonstrates that this mechanism is always in place. Younger people just need it more rarely: how often do we try out our cognitive limits, after all? But when we need it, we all have this larger cognitive resource available. Our brain is fundamentally adaptive.’
Original Publication:
Melanie S. Höller-Wallscheid, Peter Thier, Joern K. Pomper, Axel Lindner: Bilateral Recruitment of Prefrontal Cortex in Working Memory Is Associat-ed with Task Demand but Not with Age. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (electronic publication ahead of print).
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1601983114
Contact the author:
PD Dr. Axel Lindner
University of Tübingen
Hertie Institute for Clinical Brain Research
Otfried-Müller-Str. 25
72076 Tübingen
Phone: +49 7071 29-0469
a.lindner@medizin.uni-tuebingen.de
Press contacts:
Dr. Paul Töbelmann
Science Communication and Public Outreach
Werner Reichardt Centre for Integrative Neuroscience (CIN)
Otfried-Müller-Str. 25
72076 Tübingen
Phone: +49 7071 29-89108
paul.toebelmann@cin.uni-tuebingen.de
www.cin.uni-tuebingen.de
Dr. Mareike Kardinal
Head of Communications
Hertie Institute for Clinical Brain Research
Otfried-Müller-Str. 27
72076 Tübingen
Phone: +49 7071 29-88800
Fax: +49 7071 29-25004
mareike.kardinal@medizin.uni-tuebingen.de
www.hih-tuebingen.de
http://www.hih-tuebingen.de Hertie Institute for Clinical Brain Research
http://www.cin.uni-tuebingen.de Werner Reichardt Centre for Integrative Neuroscience (CIN)
http://www.uni-tuebingen.de University of Tübingen












