
Ötzi the Iceman: Researchers validate the stability of genetic markers
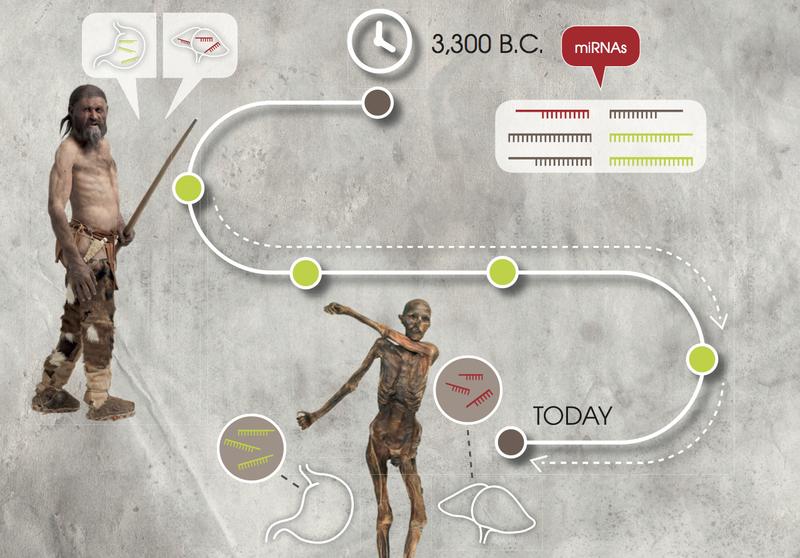
Researchers found short ribonucleic acid molecules (microRNA) even in mummies like Ötzi.
Andreas Keller, Universität des Saarlandes
A number of facts have been scientifically proven about the glacier mummy, known as “the Iceman” or “Ötzi,” found in the Ötztal Alps (South Tyrol) in 1991. Through imaging techniques, we know about degeneration in his lumbar spine and a fatal arrow wound in his left shoulder. DNA analyses showed that Ötzi was lactose intolerant, and had brown eyes and blood type 0. Now a study of Ötzi's microRNAs has also been completed. MicroRNAs are very small pieces of ribonucleic acid (RNA) and play a central role in the regulation of genes.
Although these molecules are very stable in tissues, prior to this study it was unclear whether they could still be found in human tissues after thousands of years. Therefore, Professors Andreas Keller and Eckart Meese of Saarland University, Stephanie Kreis of the University of Luxembourg, and Professor Albert Zink and Frank Maixner of Eurac Research in Bozen took on the challenge.
They analyzed not only tissue samples from the Iceman, but also those from a mummy of a soldier fallen in World War I. “Our investigation provides evidence that we can analyze microRNA even after thousands of years,” explains Andreas Keller, Professor of Clinical Bioinformatics at Saarland University, who coordinated the study.
The scientists took samples from Ötzi's skin, stomach, and stomach contents. “It was a challenge to extract this genetic material in significant quantities and sufficient quality from the mummified tissue samples, and to measure and quantify it with the newest, very precise methods,” reports Stephanie Kreis, who isolated the microRNAs at the University of Luxembourg.
Some molecules were found that were present predominantly in the ancient tissues. Conversely, some of the biomarkers that are well-known today were not found in Ötzi. According to Professor Zink from Eurac Research, the microRNAs are the next important class of molecules from Ötzi to receive intensive examination.
Professor Meese, head of the Institute of Human Genetics at Saarland University, claims that the stability of these biomarkers is also important for people today. “It is vital for clinical applications,” explains Meese.
“It's evident that the potential of microRNA is much greater than we previously thought. We still don't know enough about how these molecules influence specific genes, entire gene families, or biochemical reaction pathways. When we investigate this further, it's possible microRNAs will become new stars in therapy. Until then, however, there is a lot more work to do,” concludes Professor Keller.
Further information:
Publication
“miRNAs in ancient tissue specimens of the Tyrolean Iceman”
https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw291
Questions can be directed to:
Professor Andreas Keller
Chair for Clinical Bioinformatics
Saarland University
Tel.: +49 681 302 68611
E-mail: andreas.keller@ccb.uni-saarland.de
Professor Albert Zink
Institute for Mummies and the Iceman
Eurac Research
Tel.: +39 0471 055561
E-mail: albert.zink@eurac.edu
Dr. Stephanie Kreis
Life Sciences Research Unit
University of Luxembourg
Tel.: +352 4666 44 6884
E-mail: stephanie.kreis@uni.lu
Editor:
Gordon Bolduan
Competence Center of Computer Science Saarland
Saarland Informatics Campus E1.7
Saarland University
Tel.: +49 681 302 70741
E-mail: gbolduan@mmci.uni-saarland.de
https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw291












