
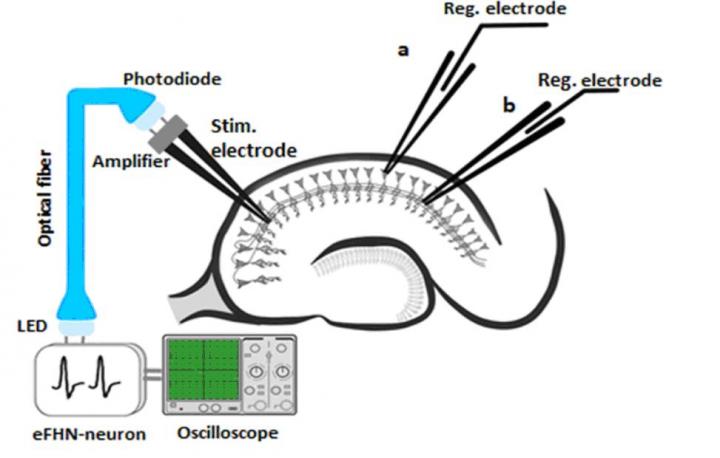
This is a schematic illustration of an optoelectronic device during the stimulation of synaptic transmission in the mouse hippocampus section.
Credit: Lobachevsky University
In the past few decades, research aimed at finding approaches to restoring brain function has increased exponentially. An interdisciplinary approach to the task of brain function restoration combines complementary approaches and methods of regenerative medicine, on the one hand, and those proposed by neuroengineering, on the other.
Biological approaches are based on activating the regenerative capacity of the brain and on cell transplantation, whereas engineering strategies include methods of neuromodulation, creating replacement or bridge neuroprostheses or developing brain-machine interfaces. The engineering approach is to create a biohybrid architecture that somehow connects the artificial control device with the brain: it hinders neuronal activity or, on the contrary, initiates this activity.
According to Svetlana Gerasimova, junior researcher at the Physics and Technology Research Institute and at the Neurotechnology Department of Lobachevsky University (Nizhny Novgorod, Russia), Russian scientists together with their colleagues from the Technical University of Madrid (Spain) have first proposed and developed an optoelectronic interface for the interaction of electronic neuron-like generators and living neurons of the brain (Fig.1).
“The designed interface differs from the existing methods of acting on brain neurons: it uses a fiber-optic channel to transmit signals from an artificial electronic neuron to a live one (Fig. 2). At the same time, unlike in the known optogenetics methods, there is no need to perform technically difficult and expensive genetic modifications of neurons for stimulation. Stimulation of living neurons is carried out with the help of an electrical signal obtained using photoelectric conversion at the output of the optical fiber,” Svetlana Gerasimova says.
Mikhail Mishchenko, researcher at the Department of Oscillation Theory and Automatic Control of the UNN Faculty of Radiophysics, notes that the main advantage of using optical fiber instead of traditional metal wires is galvanic isolation, which rules out the possibility of electrical damage to brain tissue due to breakdown or electromagnetic effects.
“Besides, optical fiber provides another important advantage: the effectiveness of the interface in terms of affecting brain neurons can be increased by using an active optical fiber instead of a passive one. Thus, adaptive stimulation will be possible and its effectiveness will depend on the current state of the fiber optic channel, which reproduces the effects of synaptic plasticity,” concludes Mikhail Mishchenko.
The effectiveness of the proposed system in stimulating the electrophysiological activity of neurons in a surviving section of the hippocampus has been demonstrated. It can be used to develop adaptive systems for restoring brain activity or replacing individual parts of the brain affected by an injury or a neurodegenerative disease.















