
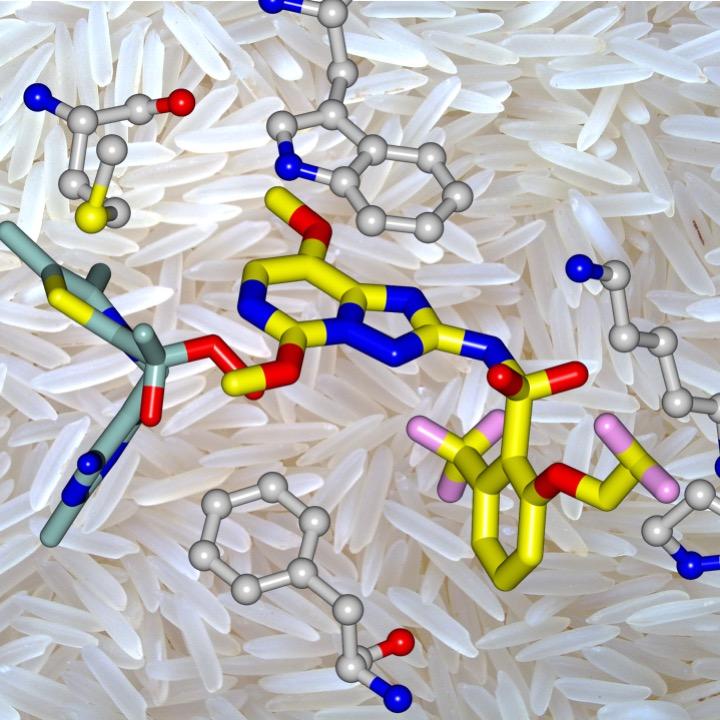
Penoxsulam, in yellow, binds to the surface of the enzyme (acetohydroxyacid synthase). Penoxsulam is a leading herbicide for crop protection especially for rice (background) and wheat.
Credit: Courtesy the research team
Usage Restrictions: For use with this article
A UQ School of Chemistry and Molecular Biosciences study led by Associate Professor Luke Guddat uncovered how penoxsulam, the active ingredient in the world's largest-selling rice herbicide, works.
“Penoxsulam controls weeds such as key grass, broadleaf and sedge, and has become a focus of research due to an increased number of weeds that have developed resistance to herbicides,” Dr Guddat said.
“Understanding how it works will assist in managing herbicide resistance not only for rice growers but also for wheat, turf and wine producers globally.
“These compounds have been shown to have extremely low levels of toxicity to the environment.”
The researchers hope the discovery will contribute to the design of the next generation of safe and commercially effective herbicides to counter the growing number of weeds becoming resistant.
Herbicide-resistant weeds result in lost income for the world's crop producers despite the $30 billion they spend on herbicides each year, threatening food security.
The research conducted by Dr Thierry Lonhienne and PhD student Mario Garcia used crystallographic studies to capture the molecular mechanisms of the herbicide in action.
“We discovered penoxsulam combines with an enzyme in the weed and prevents it from carrying out its normal function, which is to produce amino acids, the fundamental building blocks of proteins.” Dr Guddat said.
“Luckily, humans and other animals don't have that enzyme so penoxsulam compounds are relatively safe at the concentrations used in field applications.”
###
The study, published in PNAS (doi: 10.1073/pnas.1714392115), was funded by the National Health and Medical Research Council.
Dr Guddat and UQ colleagues Professor Craig Williams and Professor Gimme Walter have now been awarded funding to study weed-resistant herbicides to combat weeds of significance in Australia.












