
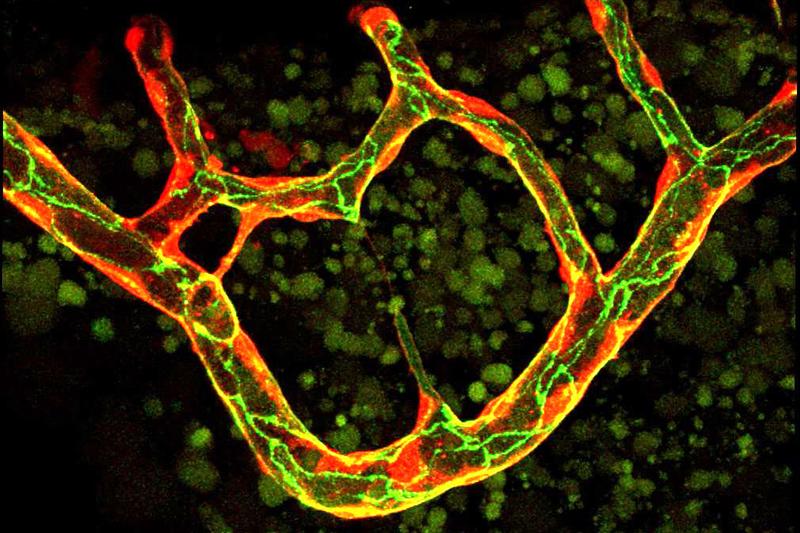
Blood vessel network of the zebrafish during the remodeling phase. Some of the small thin branches will regress to form a simpler vessel pattern.
Biozentrum, University of Basel
The vascular system is the supply network of the human organism and delivers oxygen and nutrients to the last corners of the body. So far, research on the vascular system has focused primarily on the formation of such vascular networks.
Markus Affolter’s research group at the Biozentrum of the University of Basel has now investigated the blood vessel pruning in the zebrafish and discovered that the cells have the ability to self-fuse at the membrane margins. Previously, it was unknown that blood vessel cells of vertebrates have this property.
Self-fusion observed in vertebrates for the first time
The formation of blood vessels follows a complicated architectural plan. “At a first glance, the plan for vascular regression seems to be the same but it must differ at the molecular level”, explains Markus Affolter. During vascular regression, most of the cells consecutively migrate and incorporate into the neighboring functional vessels.
The last single cell that remains in the pruning vessel reaches around the lumen and the membrane margins of this cell undergo fusion thus closing the vessel and assuring its tightness. This process, named cell self-fusion, ensures a controlled closure of a regressive blood vessel thus preventing blood leakage. For the first time this self-fusion of cells has been observed in vertebrates, the group humans also belong to. “Such cell behavior was so far only known in simpler organisms such as nematodes”, explains Markus Affolter.
Greater plasticity through self-fusion
During the development of the vascular network, blood vessels are constantly formed but many of them are only required temporarily. Just like a disused arm of a highly branched river, the flow of fresh blood through these vessels is interrupted and the organism begins to prune this side arm. In this way the vascular system regulates itself, optimizing its blood circulation by pruning and recycling the unnecessary vessels with reduced blood flow and blood pressure.
“This newly uncovered process is important for the understanding of blood vessel formation and regression on the cellular level, as this can also explain the extraordinary plasticity and changeability of the vascular system”, says Anna Lenard, the first author of this publication. These investigations were performed on the zebrafish, as in this almost transparent fish the development of blood vessels can be observed in the living animal using modern microscopy techniques.
Relevance of self-fusion for cancer?
“How the cell recognizes its own membrane margins and how fusion with neighboring blood vessel cells is prevented, is not yet known”, says Markus Affolter. Since a long time it has been postulated that each individual cell of an organism has its own code.
“The regression process could partly confirm this theory”, thinks Markus Affolter. Together with his team, he would like to investigate the self-fusion process more closely. As tumors require a well developed vascular system for their growth, a better understanding of the formation and regression of this network could open possibilities for the manipulation of such a system.
Original article:
Anna Lenard, Stephan Daetwyler, Charles Betz, Elin Ellertsdottir, Heinz-Georg Belting, Jan Huisken, Markus Affolter:
Endothelial Cell Self-fusion during Vascular Pruning.
PLoS Biology published online 17 April 2015 | DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002126
Further information:
Heike Sacher, Biozentrum Communications,Tel. +41 61 267 14 49, E-Mail: heike.sacher@unibas.ch University of Basel
https://www.unibas.ch/en/News-Events/News/Uni-Research/Pruning-of-blood-vessels….












