
Stress in the cerebellum – a signaling molecule is critical for the motor ability
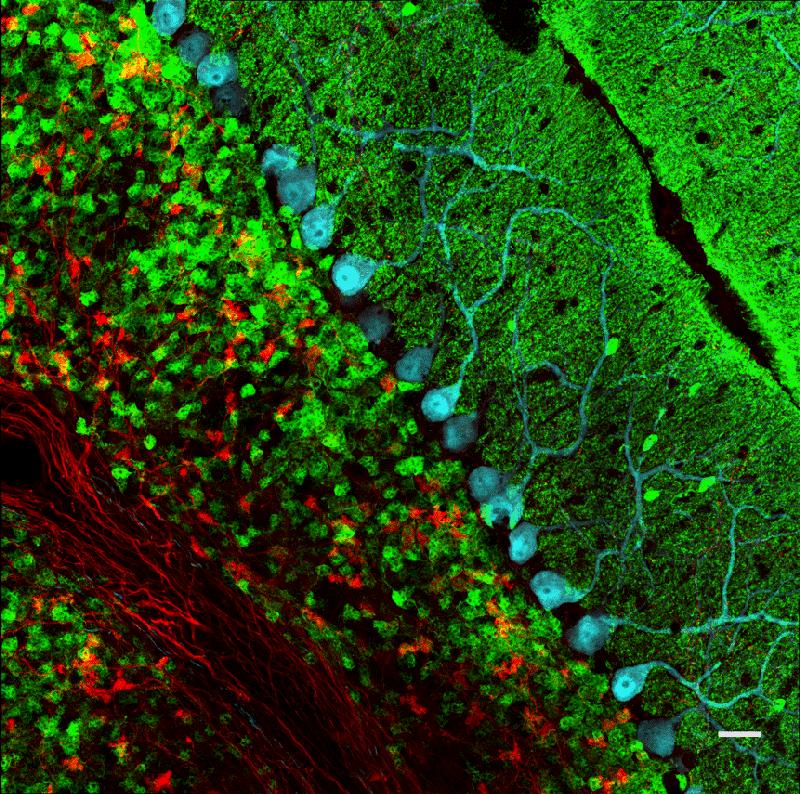
Sagittal section of the cerebellum. CRFR1 (red) expressed in granule cells (green), which are reached by CRH positive fibers (red). Purkinje neurons are shown in blue.
© MPI of Psychiatry / Gili Ezra-Nevo, 2018
In the first study, published recently in Translational Psychiatry, researchers investigated the stress neuropeptide CRF in a region of the brain called the inferior olive. The inferior olive is found in the brain stem and is one of the major inputs to the cerebellum, sending climbing fibers to Purkinje cells. It was known that CRF is highly expressed in inferior olive neurons both in mice and humans. However, no research had looked at the role of these neurons in behavior or physiology.
Using a mouse model with lowered levels of CRF only in the inferior olive neurons, the scientists could investigate its specific role. First author and a former PhD student of the Institute´s director Alon Chen, Gili Ezra-Nevo explains “we were able to show that CRF in these neurons is critical for the motor ability of the mouse but only under challenging conditions and not for general locomotion.”
Deleted receptor
In the second study, published in The Journal of Neuroscience, the researchers investigated the CRF type 1 receptor (CRFR1) in the cerebellum. Again, it was known that CRFR1 is highly expressed in the cerebellum, but little was known about its function.
In another mouse model, scientists deleted CRFR1 in the granular cells of the cerebellum and explored the behavioral and cellular consequences. They found a profound effect on learning both at the cellular and behavioral levels without any effect on baseline motor skills. The granular cell deletion changed long-term potentiation and the expression of calcium signaling components.
Alon Chen, Director at the Institute and heading these two projects concludes: “These studies highlight the CRF system’s central role in cerebellar functioning. Patients with stress-related pathologies show altered cerebellar connectivity, so understanding how stress can affect motor function and learning is important.”
Inferior olive CRF plays a role in motor performance under challenging conditions.
Ezra-Nevo G, Volk N, Ramot A, Kuehne C, Tsoory M, Deussing J, Chen A.
Translational Psychiatry
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-018-0145-3
Cerebellar Learning Properties Are Modulated by the CRF Receptor.
Ezra-Nevo G, Prestori F, Locatelli F, Soda T, Ten Brinke MM, Engel M, Boele HJ, Botta L, Leshkowitz D, Ramot A, Tsoory M, Biton IE, Deussing J, D'Angelo E, De Zeeuw CI, Chen A.
The Journal of Neuroscience
https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3106-15.2018
https://www.mpg.de/12217851/stress-in-the-cerebellum












